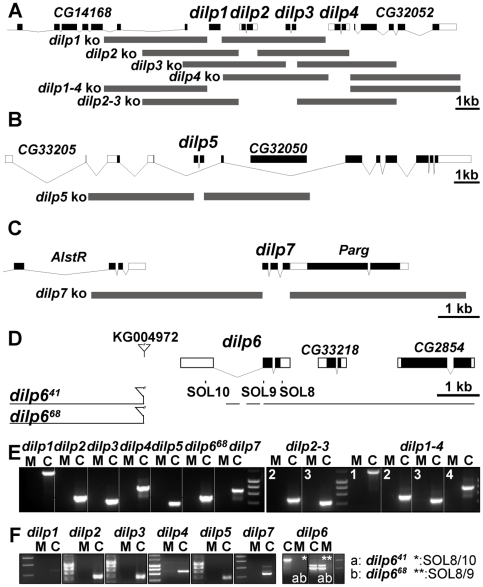
Figure 2. Gene locus organization and generation of dilp mutants.
(A–C) Null mutations for dilp1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 2–3, and 1–4 were generated by ends-out homologous recombination and by imprecise P-element excision for dilp6 (D). (A) The dilp1–4 genes cluster at cytological position 67C8 is separated from dilp5 by two intervening genes of unknown function (Flybase: CG32052 and CG33205). (B) dilp5 is located within an intron of the CG33205 gene. (C) dilp7 is located on the X-chromosome at 3E2 immediately downstream of the essential Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (Parg) gene. Donor constructs (dilp ko) for ends-out homologous recombination are indicated by grey bars. Gap between grey bars indicates the genomic region replaced by a whitehs marker gene. Coding parts of exons are marked in black, non-coding parts by white boxes. (D) Transposon integration line KG004972 was used to generate dilp6 deletion mutants dilp641 and dilp668. Note: both dilp6 deletion alleles contain remaining P-element sequence, hatched line: region of breakpoint in dilp641. (E) PCR on genomic DNA of dilp mutants with dilp specific primer combinations shows homologous recombination mediated replacement of dilp genes by the whitehs marker gene and deletion of dilp6 in dilp668 mutants (M: mutant, C: control). (F) RT–PCR analysis confirms that dilp mutants are transcript null alleles. dilp641 mutants express ectopic dilp6 transcripts that lack the first exon but contain the full ORF. dilp668 mutants are dilp6 transcript null alleles.