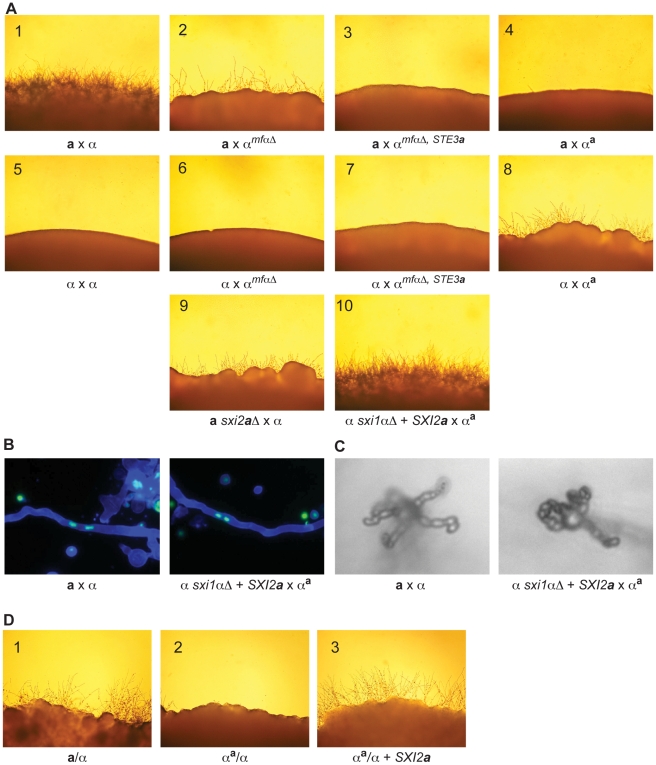
Figure 4. α x αa crosses proceed through sexual development only in the presence of Sxi2a.
(A) Sexual development assays were carried out on V8 for 72 hours, and the peripheries of crosses are shown under 200× magnification. Panels: 1) a x α, 2) a x αmfαΔ, 3) a x αmfαΔ, STE3a, 4) a x αa, 5) α x α, 6) α x αmfαΔ, 7) α x αmfαΔ, STE3 a, 8) α x αa, 9) a sxi2 a Δ x α, 10) α sxi1αΔ + SXI2 a x αa. Complete sexual development is observed only in panels 1 and 10. (B) Dikaryotic filaments are produced in the α sxi1αΔ + SXI2 a x αa cross. Calcofluor stained filaments appear blue, and Sytox Green strained nuclei appear green. Both an a x α cross (left) and the α sxi1αΔ + SXI2 a x αa cross (right) produce dikaryotic filaments (400× magnification). (C) Basidia and spores are produced in the α sxi1αΔ + SXI2 a x αa cross. High resolution microscopy reveals the formation of basidia and spores from an a x α cross (left), and from the α sxi1αΔ + SXI2 a x αa cross (right) (1000× magnification). (D) Addition of the SXI2 a gene to αa/α diploids results in sexual development. Diploids were incubated on V8 for 72 hours, and test spot peripheries are shown under 200× magnification as follows: wild type a/α diploid (panel 1), αa/α diploid (panel 2), and αa/α + SXI2 a (panel 3).