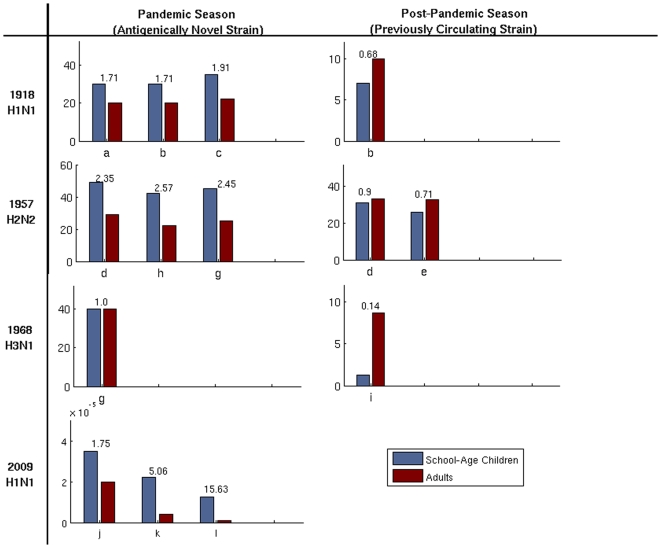
Figure 3. Attack rates among adults and children during influenza pandemics and subsequent seasons.
Multiple bars for a single strain represent data from different populations. Data are from a: [62], b: [61], c: [66], d: [67], e: [68], f: [69], g: [70], h: [71], i: [72], j: [73], k: [74], l: [38]. Numbers above bars represent odds ratios. While there are consistent qualitative patterns, the estimates are based on diverse data and methodologies and thus should not be compared quantitatively across studies. The 1968 Hong Kong H3N2 pandemic is the only one of the four strains that does not appear to have an initial bias towards children, which may be influenced by cross immunity from prior H2N2 infections as the two viruses shared nearly identical neuriminidase molecules [75]. Data for H1N1/09 is reported as number of confirmed cases as a proportion of age group size in the respective country.