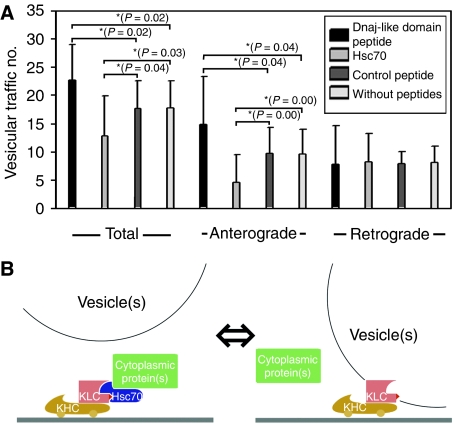
Figure 4.
DnaJ-like domain peptide treatment and vesicular transport in squid giant axons. (A) The number of vesicles passing across the fixed line with a unit length (10 μm) for 1 min, both antero- and retrogradely in VEC-DIC images. (Left) Total vesicular traffic (both antero- and retrograde transport) was promoted by DnaJ-like domain peptide application, and inhibited by Hsc70 treatment, when compared with control peptide applied or untreated specimen. (Middle) Anterograde vesicular traffic was increased in the presence of DnaJ-like domain peptide, and inhibited by Hsc70 in the same way as the cases shown in the left column. (Right) Retrograde vesicular traffic was not affected by peptide or Hsc70 treatments. Bars indicate standard deviations. Pairs with asterisk indicate their P-values are <0.05 (Mann–Whitney tests, n=16 for each). (B) DnaJ-like domain of KLC serves to anchor KLC to Hsc70. (Left) Slow axonal transport mode. By associating with DnaJ-like domain in the TPR of KLC, activated Hsc70 binds to cytoplasmic proteins. (Right) Fast axonal transport mode. The same domain binds to a membranous vesicle.