Figure 1.
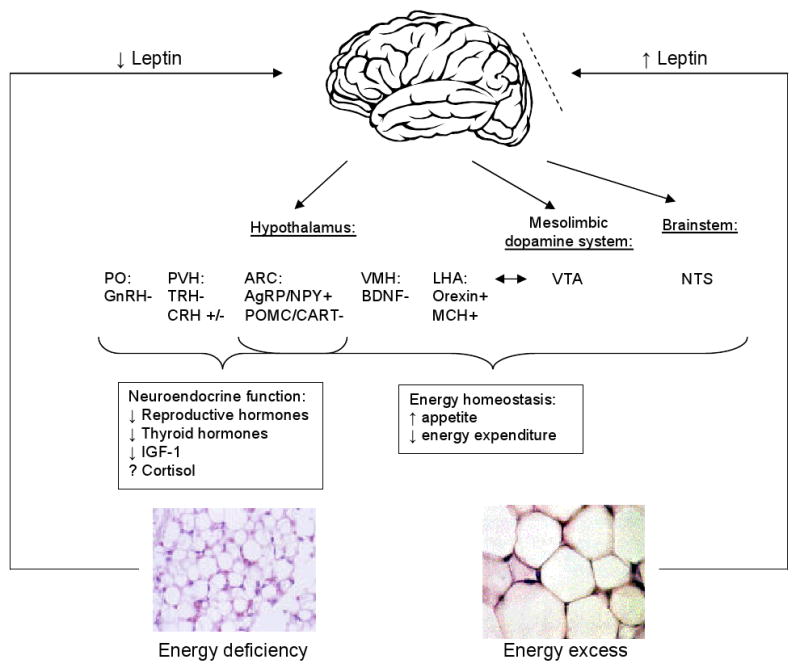
The central effects of leptin in states of energy excess and deficiency. States of energy excess are associated with hyperleptinemia but the hypothalamus is resistant or tolerant to the effects of increased leptin, represented by the dashed line. Energy deficiency results in hypoleptinemia. As a result, a complex neural circuit comprising of orexigenic and anorexigenic signals is activated to increase food intake (17). There is increased expression of orexigenic neuropeptides: AgRP and NPY in the ARC (23) and orexin and MCH in the LHA. Furthermore, there is decreased expression of anorexigenic neuropeptides: POMC and CART in the ARC (23) and BDNF in the VMH. In addition to neurons that project from the LH to the VTA, leptin also acts at the VTA of the mesolimbic dopamine system to regulate motivation for and reward of feeding. Leptin activation of the NTS of the brainstem also contributes to satiety. In addition, leptin has direct and/or downstream effects on the PVN and PO that are important for neuroendocrine responses to energy deprivation, including decreasing reproductive and thyroid hormones. While leptin only acts indirectly on the GnRH-secreting neurons in the hypothalamus, it can act directly and indirectly on TRH-secreting neurons (17). The effect of leptin on cortisol levels during starvation differs in mice and humans. Unlike in normal mice (24), leptin administration does not reverse the elevated ACTH levels associated with starvation in humans (7). The mechanism of leptin's effect on the growth hormone axis is unclear.
Abbreviations: AgRP, Agouti-related Protein; NPY, Neuropeptide Y; ARC, arcuate nucleus; MCH, Melanin-concentrating Hormone; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; POMC, Proopiomelanocortin; CART, Cocaine- and Amphetamine-regulated Transcript; BDNF, Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus; VTA, ventral tegmental area; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; PO, preoptic area; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; TRH, thyrotropin-releasing hormone; ACTH, adrenocorticotropin.
