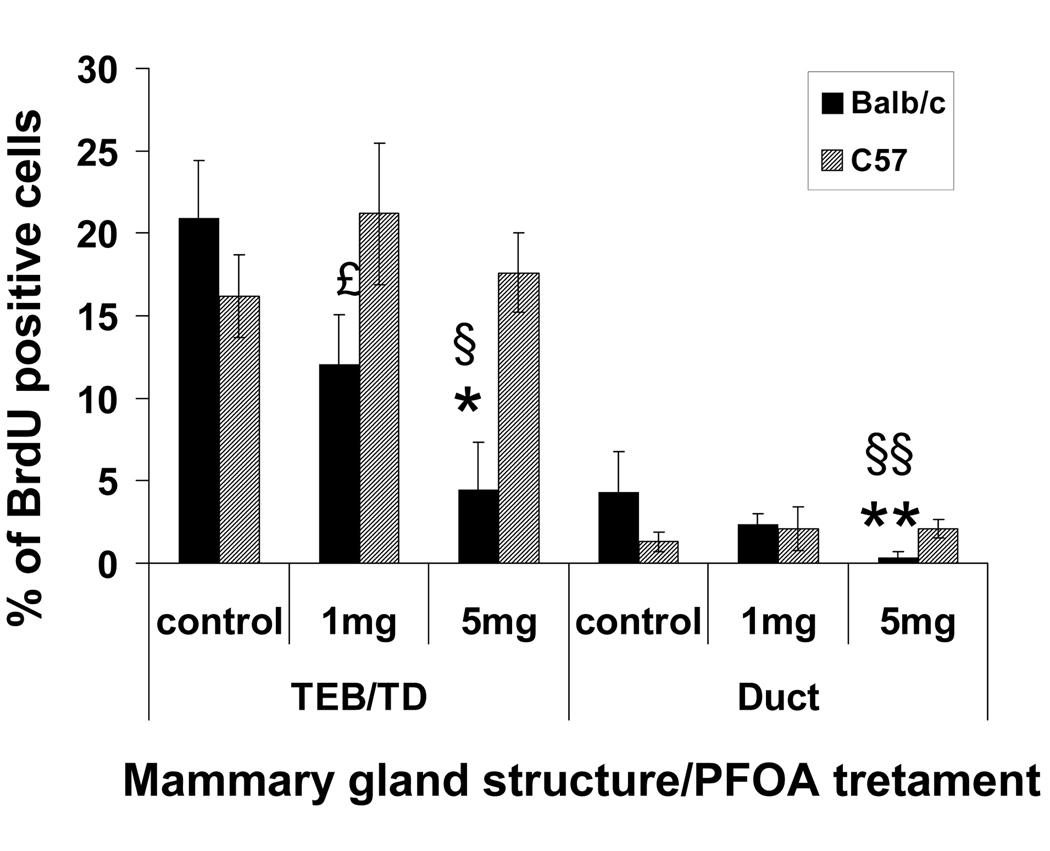
Fig. 2. Effect of PFOA treatment on mouse mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation.
Mouse mammary epithelial cell proliferation was determined by BrdU incorporation assay. Two h before killing, mice were injected with BrdU (70 mg/kg of body weight). BrdU incorporation was detected in histological sections by immunoflourescence staining as described in Materials and Methods. Cell proliferation was quantitated in TEBs, stimulated TDs and ducts by counting the number of BrdU positive luminal epithelial cell nuclei from captured images using MetaMorph software as described in Materials and Methods. Five mice per treatment group were analyzed, and a minimum of 1000 total cells and three independent sections per mouse were analyzed. The values for TEBs and stimulated TDs were combined. Data are presented as Mean ± S.E.M. (n=5). * p<0.05 compared with vehicle-treated Balb/c TEB/TD; ** p<0.05 compared with vehicle-treated Balb/c duct; £ p<0.05 PFOA (1mg/kg)-treated C57BL/6 TEB/TD compared with PFOA (1 mg/kg)-treated Balb/c TEB/TD; § p<0.05 PFOA (5mg/kg)-treated C57BL/6 TEB/TD compared with PFOA (5 mg/kg)-treated Balb/c TEB/TD; §§ p< 0.05 PFOA (5mg/kg)-treated C57BL/6 duct compared with PFOA (5 mg/kg)-treated Balb/c duct.