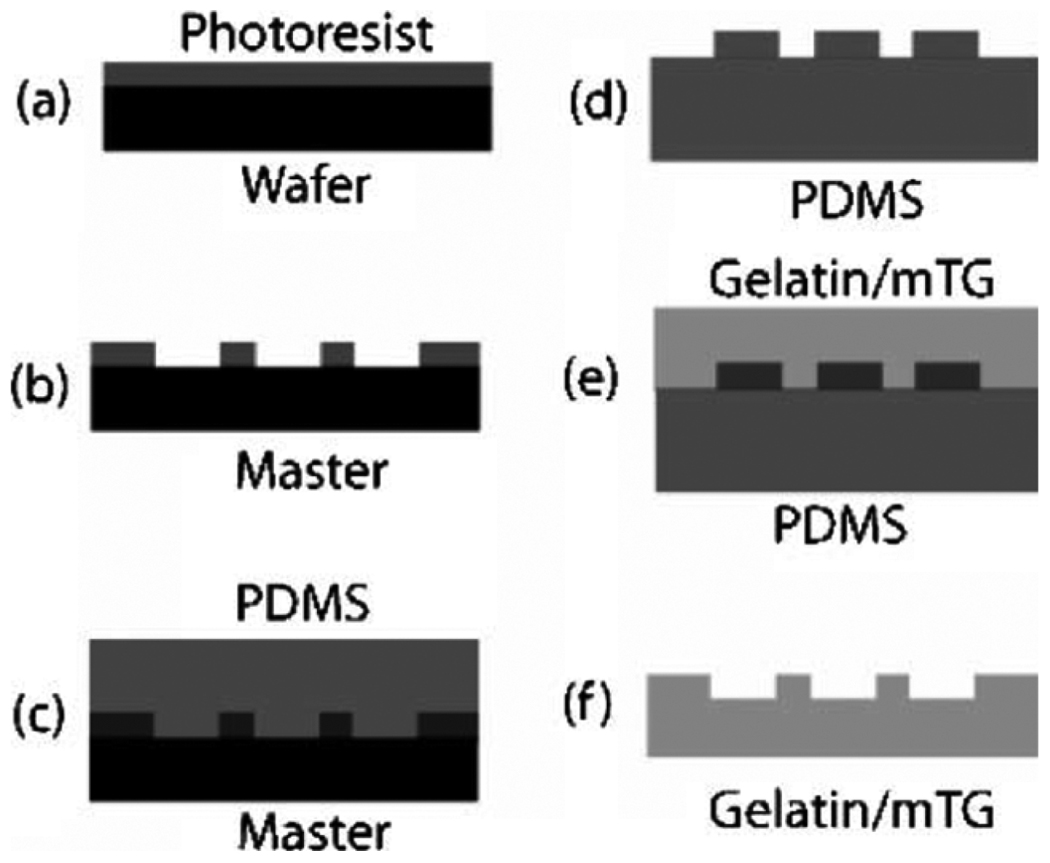
Fig. 8.
Schematic of PDMS device/mold fabrication from a mold created using (a)–(c) photolithography and (d)–(f) subsequent manufacture of a gelatin device from a PDMS mold using soft lithography. Photoresist is typically spin coated onto a (a) silicon wafer. (b) The photoresist is exposed to UV through a photomask, and unpolymerized photoresist is removed in a developing solvent to produce a master. PDMS is then cured on (c) this master and used as (d) a mold for gelatin. The gelatin and enzyme solution is then poured over (e) the reusable, flexible PDMS mold and the polymerized device is then (f) pulled off the mold [73]. (Figure reproduced by the permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2006.)