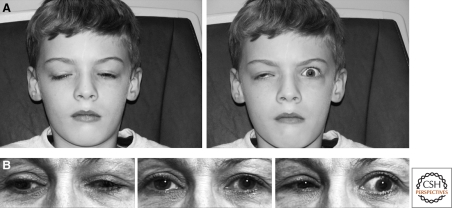
Figure 1.
Ocular synkinesis. (A) Child with CFEOM1 and Marcus Gunn jaw-winking phenomenon harboring a KIF21A mutation. His superior branch of the oculomotor nerve is hypoplastic/absent, resulting in bilateral ptosis from lack of appropriate innervation of the levator palpebrae superioris (LPS) muscle, and a downward position of each eye from absent innervation of the superior rectus muscle (left). Marcus Gunn phenomenon (right) is seen as the synkinetic elevation of the left eyelid with a subtle change in jaw position associated with a volitional increase in pterygoid muscle tension. This results from aberrant innervation of the LPS by axons from the motor branch of the trigeminal nerve that also innervates the intended ipsilateral pterygoid muscle. (B) Adult with Duane retraction syndrome harboring a CHN1 mutation. Central gaze reveals mild exotropia (middle). On attempted right gaze (left) and left gaze (right), there is limited horizontal excursion with globe retraction and secondary palpebral fissure narrowing of the adducting eye. Globe retraction results from synkinesis of the medial and lateral recti muscles. (A) Modified with permission from Yamada et al. 2005. Copyright © (2005) American Medial Association. All rights reserved. (B) Modified from Demer et al. 2007. Copyright © (2007) Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology. All rights reserved.