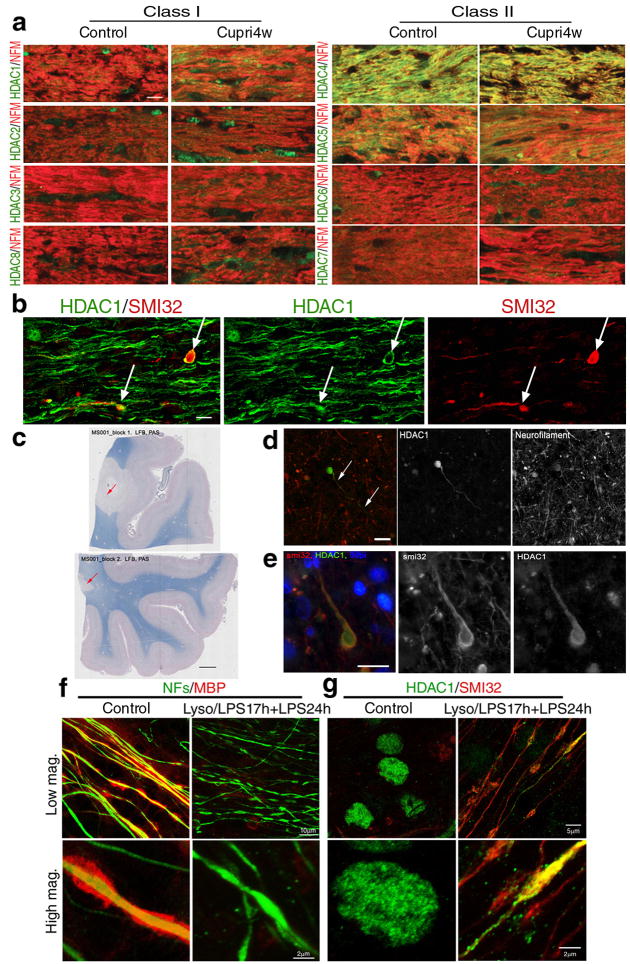
Figure 1. Cytosolic HDAC1 is detected in animal models of demyelination, in the brain of MS patients and in demyelinated slice cultures.
(a) Confocal micrographs of the corpus callosum of control and 4 week cuprizone-fed mice (Cupri4w), stained with antibodies specific for class I (HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, HDAC8) and class II HDAC isoforms (HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC6 and HDAC7), indicated on the left (green) and with anti-neurofilament medium chain antibody (NFs, red). Scale bar 10 μm; 63× objective. (b) Confocal image of the co-localization (white arrows) of hypophosphorylated neurofilament heavy chain (SMI32, red) and HDAC1 (green) in damaged axons in the corpus callosum of cuprizone fed mice. Scale bar 5 μm. (c) Luxol fast blue/periodic acid Schiff staining of human brain sections identified areas of white matter demyelination (arrows, scale bar 200 μm). (d) Serial sections of the same lesions were used to show the presence of HDAC1+ end bulbs (green) in neurofilament positive (red) axons. Scale bar 10 μm. (e) Adjacent sections were processed for immunohistochemistry with antibodies for SMI32 (red) and HDAC1 (green) in white matter lesions. DAPI (blue) was used as nuclear counterstain. Scale bar 10 μm. (f) Confocal images of cerebellar slice cultures either untreated (Control) or treated with lysolecithin and LPS to induce demyelination (Lyso/LPS17h+LPS24h). Cultures were stained with antibodies specific for myelin basic protein (MBP, red) and NFs (green) antibodies. (g) The same cultures were then stained for HDAC1 (green) and SMI32 (red).