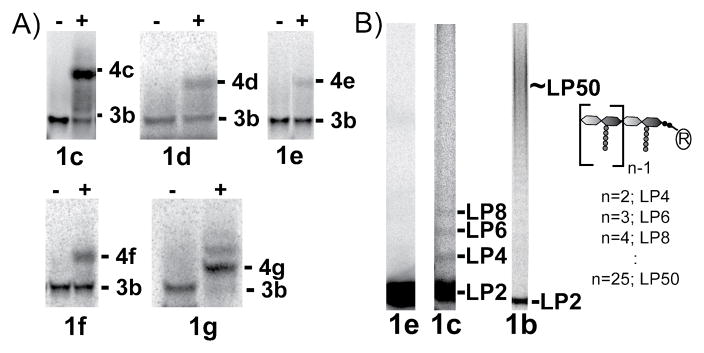
Figure 3. SDS-PAGE analysis of the acceptor site assay (A) and the homopolymerization assay (B).
A) [14C]-3b and [14C]-1c–g were incubated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of AaPBP1A.2a In all cases, predominantly one product was formed, GLP6 (4c–g). B) Comparison of the homopolymerization of 1e, 1c, and 1b by AaPBP1A. The C10 derivative (1e) cannot be homopolymerized, while the C20 (1c) and C35 (1b) derivatives are homopolymerized via a distributive and a processive mechanism, respectively.