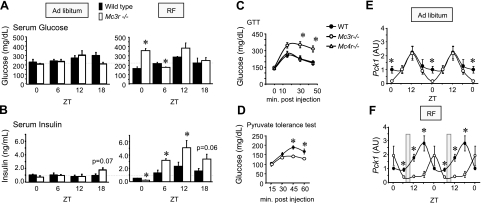
Figure 2.
Abnormal glucose homeostasis in Mc3r−/− mice subjected to RF. A, B) Serum glucose (A, left panel) and insulin (B, left panel) values in Mc3r−/− mice fed ad libitum at ZT0, 6, 12, and 18 were unremarkable. Mc3r−/− mice subjected to RF exhibited marked abnormalities in serum glucose (A, right panel) and insulin (B, right panel). At ZT0, Mc3r−/− mice subjected to RF were hyperglycemic and hypoinsulinemic (P<0.05). Hyperglycemia may have been resolved at other time points through compensatory increases in serum insulin. *P < 0.05 vs. corresponding WT. C) Mc3r−/− mice subjected to RF for 2 wk are glucose-intolerant compared with Mc4r−/− and WT mice subjected to RF. *P < 0.05 vs. WT and Mc4r−/−. *P < 0.05 vs. WT. D) Reduced conversion of pyruvate to glucose in ad libitum fed Mc3r−/− mice relative to WT mice. *P < 0.05 vs. WT. E, F) Abnormal rhythmic expression of liver Pck1 mRNA in Mc3r−/− mice is amplified during RF. In ad libitum fed animals (E), Mc3r−/− mice exhibited a lower nadir of Pck1 mRNA expression at ZT0. With RF (F), Mc3r−/− mice exhibited 3- to 4-fold lower levels of expression at ZT12 and ZT18 relative to controls. *P < 0.05 vs. corresponding WT. AU, arbitrary units.