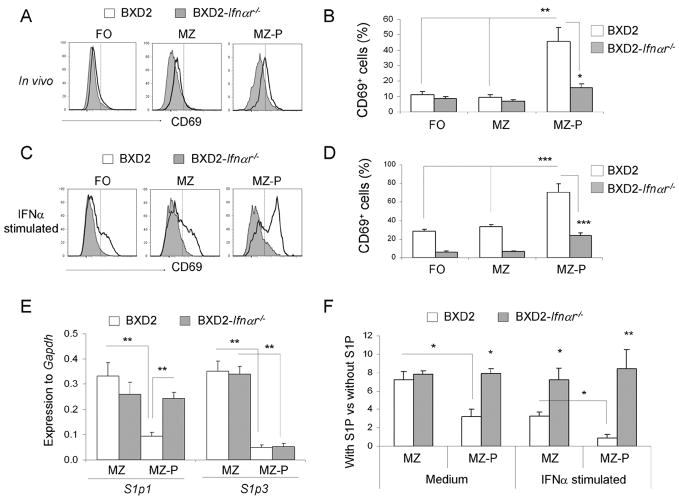
FIGURE 5.
Increased sensitivity in MZ-P B cells to type I IFN-induced CD69/S1P1 signaling. A–D, Flow cytometry analysis of the percent of CD69+ FO, MZ, and MZ-P subpopulations of B cells in the spleens of 2-mo-old BXD2 and BXD2-Ifnαr−/− mice. Single cell suspensions from the spleens of mice were A, freshly isolated, or C, stimulated with IFNα (20 ng/ml) for 12 hours, and the expression of CD69 on the indicated populations of B cells was determined. One representative experiment of a total of four samples per group is shown. B and D, Bar graph showing the expression of CD69 on each population of B cells either in vivo (B) or after stimulated with IFNα in vitro (D). Means ± SEM (n=4); * P <0.05, ** P < 0.01, or *** P <0.005 compared with wild-type BXD2 mice or compared with non-MZ-P B cell population. E, QRT-PCR analysis of S1p1 and S1p3 transcripts in FACS sorted MZ and MZ-P B cells from the spleens of the indicated strain of mice. Means ± SEM (n=4); ** P < 0.01 compared with wild-type BXD2 mice, or compared with CD23lo MZ B cell population. F, Chemotactic response on B cells from 3-mo-old BXD2 and BXD2-Ifnαr−/− mice was analyzed using a Transwell migration chamber with S1P (20 nM) or culture medium loaded in the bottom chamber. Cells were either not stimulated or stimulated with IFNα for 6 hrs prior to carrying out the migration analysis. FACS analysis was carried out to determine the migration response to S1P for the indicated populations of B cells. Means ± SEM (n=6); * P <0.05 or ** P <0.01 compared with wild-type BXD2 mice, or compared with CD23lo MZ B cells from BXD2 mice.