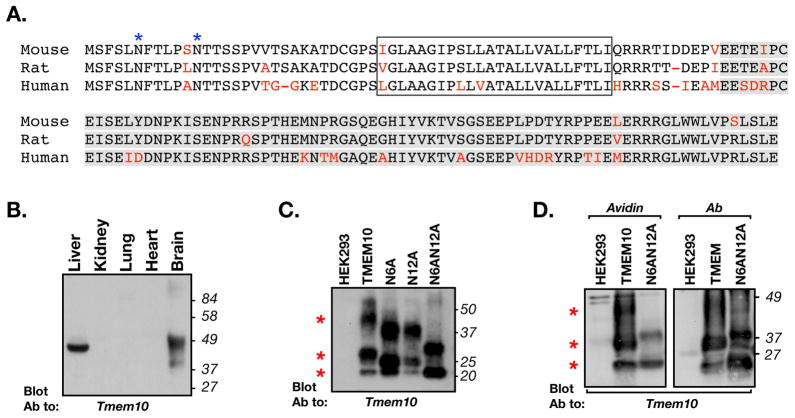
Figure 1. Tmem10 encodes for a transmembrane glycoprotein.
A. Alignment of the amino acid sequence of mouse, rat and human Tmem10 (different amino acids are shown in red. The transmembrane region is boxed and the region used to generate the antibody is highlighted in gray. The two asparagine-linked glycosylation sites found at the extracellular region of Tmem10 are labeled with blue asterisks. B. Tissue distribution. Immunoblot analysis of protein extracts prepared from the indicated tissues with an antibody to Tmem10. The location of molecular mass markers is shown on the right in kDa. C. Immunoblot analysis of glycosylation-site mutants of Tmem10. HEK293 cells transfected with an empty vector (HEK293) or cells expressing a myc-tagged Tmem10 (TMEM10), a mutant Tmem10 in which asparagine at position 6 was replaced with alanine (N6A), a mutant Tmem10 in which asparagine at position 12 was replaced with alanine (N12A), or a Tmem10 in which both asparagines were mutated to alanine (N6AN12A), were immunoprecipitated with an anti-myc antibody followed by immunoblotting with an antibody to Tmem10. Red asterisks indicate the locations of the three main bands of Tmem10. D. Cell surface biotinylation. HEK293 cells transfected with an empty vector or cells expressing a myc-tagged Tmem10 (TMEM10), or a mutant lacking its glycosylation sites (N6AN12A), were incubated with membrane impermeable NHS-biotin. Cell lysates were mixed with avidin-agarose (Avidin) or were immunoprecipitated with an antibody to myc (Ab), followed by immunoblotting with an antibody to Tmem10. Both wild type and the glycosylation mutant of Tmem10 reach the cell surface.