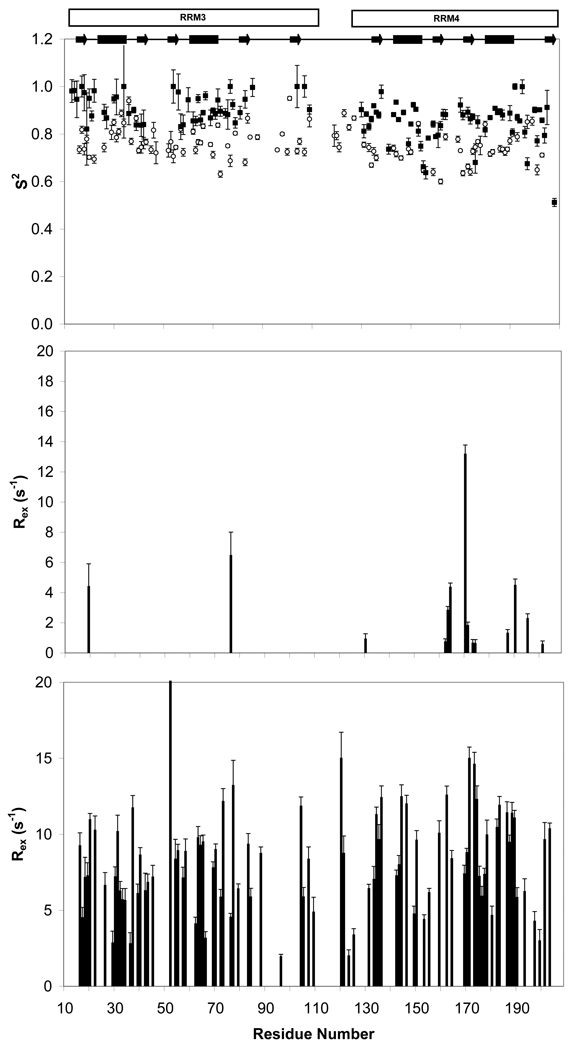
Figure 6. ModelFree analysis suggests that slow protein motions throughout PTB1:34 occur as a consequence of the RRM3/RRM4 interaction.
Lipari-Szabo order parameters, S2, are given in the top panel for PTB1:34 (○), and the individual RRMs (■). Both RRM3 and RRM4 are much more rigid alone than in the context of PTB1:34, as evident upon comparison of the exchange contribution to transverse relaxation (Rex) for PTB1:34 (bottom) and RRM3/RRM4 (middle). While PTB1:34 has uniformly dispersed Rex terms of significant magnitude throughout the protein body, only a few residues in RRM3 and RRM4 require similar Rex terms. This analysis shows that the differences in dynamic properties of the protein constructs are slow (µs-ms) motions that arise as a consequence of the RRM3/RRM4 interaction. Data were collected in 20 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 6.8, and 100 mM KCl at 500 MHz for 1 mM RRM4 and 700 MHz for 300 µM RRM3. Data for 1 mM PTB1:34 were collected at 500, 600, and 700 MHz; R2 plots for PTB1:34 are shown in Figure S4.