FIG. 2. .
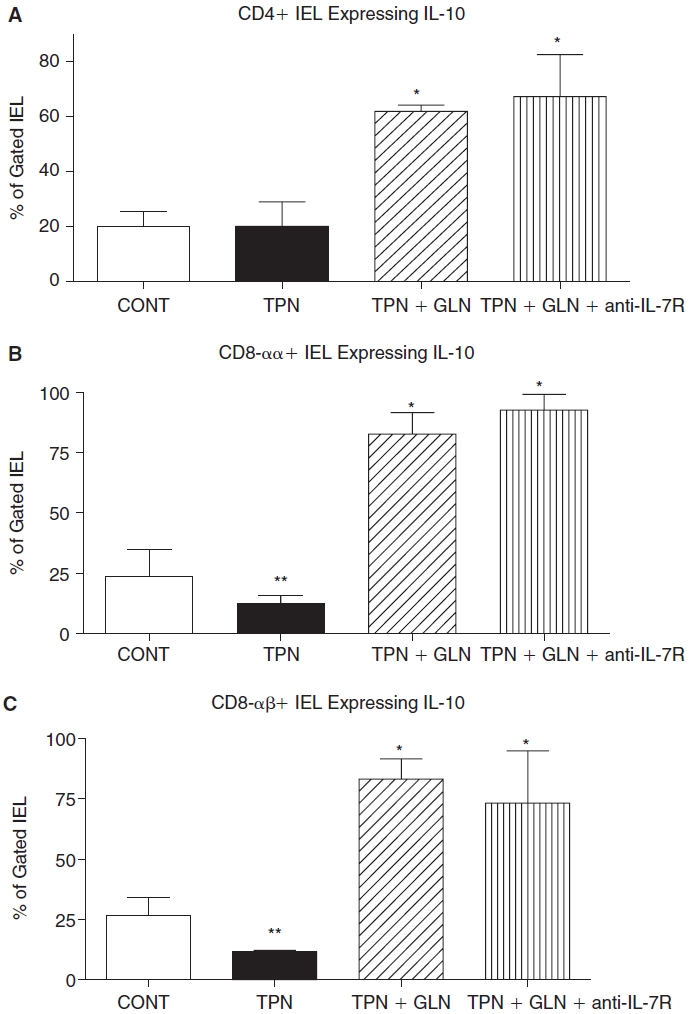
Flow cytometric results of intracellular staining for IL-10 for gated IEL subpopulations for each study group. Cell populations are expressed as the percentage of gated cells with (A) CD4; (B) CD8-α; and (C) CD8-β surface markers. TPN administration significantly decreased the percentage of CD8-αα+ and CD8-αβ+ IEL subpopulations expressing IL-10 when compared with controls. Glutamine administration significantly increased the percentage of IEL-expressing IL-10 in each subpopulation, and this increase resulted in a much greater percent expressing IL-10 compared to enteral controls. Note that TPN+GLN mice treated with IL-7R blocking antibody (TPN+GLN+anti-IL-7R) failed to change the marked increase in IEL-expressing IL-10 associated with the supplementation with glutamine. **P < 0.05 control vs. TPN; *P < 0.01 TPN+GLN (both groups) vs. control and TPN groups. N = minimum of five per group. Abbreviations: CONT, control; IEL, intraepithelial lymphocyte; IL, interleukin; TPN, total parenteral nutrition; TPN+GLN, TPN with glutamine supplementation.
