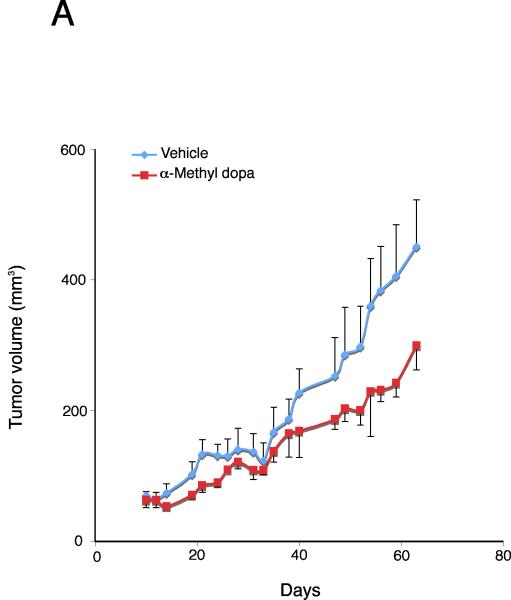
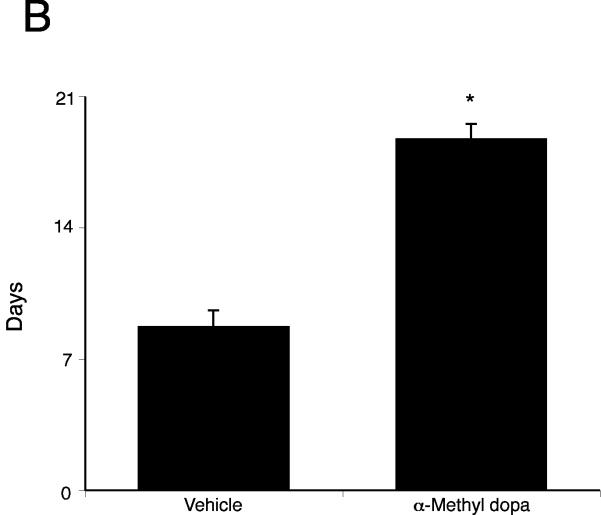
Figure 6.
Inhibition of dopamine synthesis decreases tumor growth in an in vivo xenograft model of cholangiocarcinoma. Mz-ChA-1 cells were injected into the flank of athymic mice. After tumors were established, mice were treated with 100 mg/kg/day (ip) α-methyl dopa, three days per week for 70 days and tumor volume assessed (A). Tumor latency was assessed as the time taken for the tumor to grow to 150% of the original size (B). Data are expressed as average latency (days ± SEM) and the asterisk denotes significance (p<0.05) from vehicle-treated tumors.