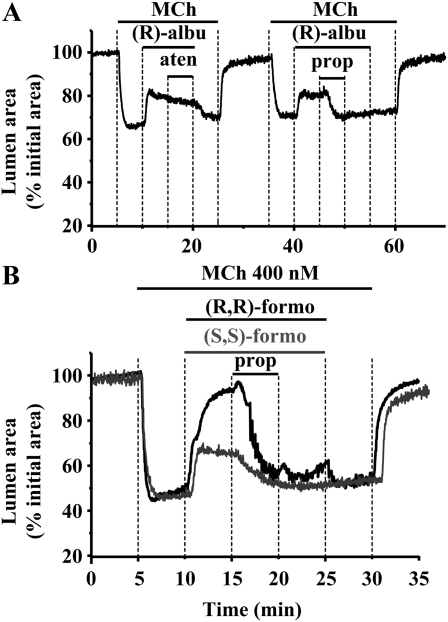
Figure 9.
Contribution of the β2-adrenoceptors to airway relaxation induced by (R)-albuterol or formoterol isomers. (A) An airway was contracted with 400 nM MCh and exposed to 1 μM (R)-albuterol to induce relaxation. The subsequent exposure to atenolol (aten; 1 μM), a specific β1-antagonist, failed to modify the response of airways to (R)-albuterol. After washing for 10 minutes with Hanks' balanced salt solutions supplemented with 25 mM Hepes, the same airway was contracted with 400 nM MCh, exposed to (R)-albuterol (1 μM) to induce relaxation, and then treated with the β1/β2–antagonist, propranolol (prop; 1 μM). Propranolol inhibited the relaxation induced by (R)-albuterol. (B) Representative experiments showing that 1 μM propranolol inhibited the relaxation induced by 1 μM (R,R)-formoterol (black line) or 2 μM (S,S)-formoterol (gray line).