Figure 2.
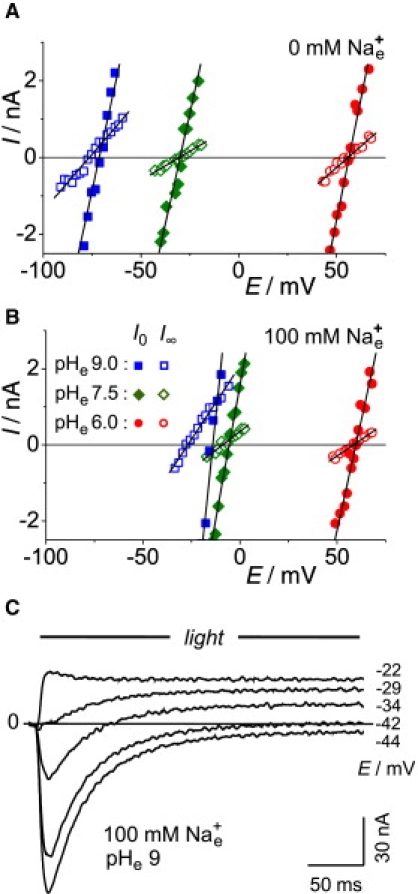
Typical experiment for determination of reversal voltages Er0 and Er∞ of ChR2 in Xenopus oocytes under various ionic conditions (in mM): internal, ∼120 Na+, ∼40 Cl−, pHc 7.3; external, 0.1 CaCl2, 2 MgCl2, and 100 mM NMGCl (A) or 100 mM NaCl (B). Voltage-clamp recordings of initial and stationary currents, I, were carried out at holding voltages, EC, in the vicinity of reversal voltages. Readings of Er are from intersections of regression lines with the zero-current line in the absence of external Na+ (A), and in the presence of 100 mM external Na+ (B) (for statistical evidence, see Fig. 4D; for quantitative analysis, see Table 1). (C) Original photocurrent records, measured at the indicated holding voltages. Note change of current sign in middle tracing (−34 mV), indicating change of reversal voltage and selectivity during a light pulse. Since the experiments in A–C were from different oocytes, the current scale in C was adjusted to match A and B.
