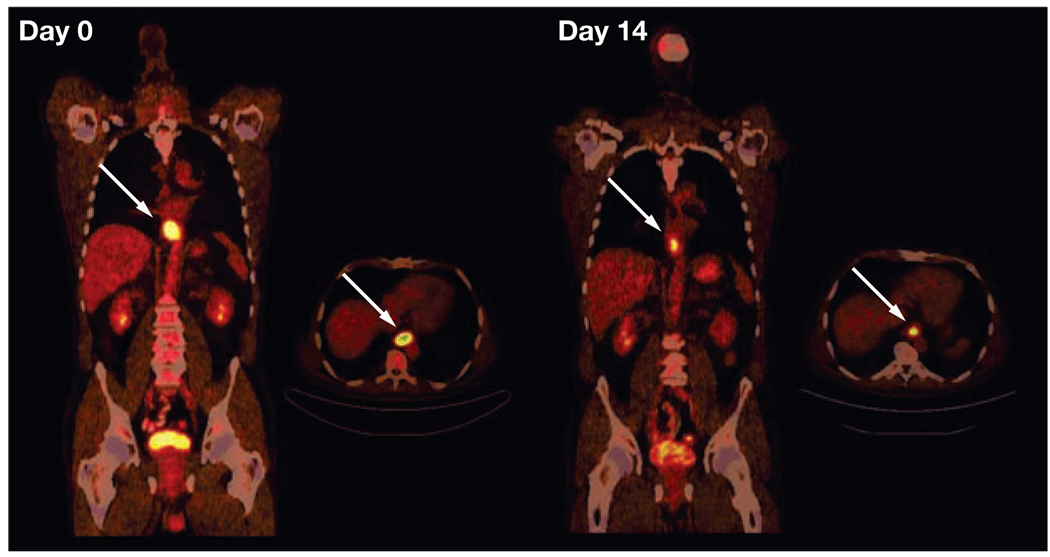
Figure 5.
Treatment monitoring with fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET and CT in a patient with locally advanced distal esophageal cancer (arrows). In each image set, the image on the left is a longitudinal section from the neck to the pelvis and the image on the right is a cross-section through the plane containing the tumor. The tumor demonstrates intense FDG uptake before therapy (day 0). FDG uptake decreases markedly on day 14 of the first chemotherapy cycle. Quantitatively, FDG uptake by the tumor decreased from a standard uptake value of 9.2 to 4.2. After completion of preoperative chemotherapy, the tumor was resected. Histopathology demonstrated less than 10% of viable tumor cells in the resected specimen. Permission obtained from the American Society of Clinical Oncology © Weber WA (2006) Positron emission tomography as an imaging biomarker. J Clin Oncol 24: 3282–3292.