Figure 3.
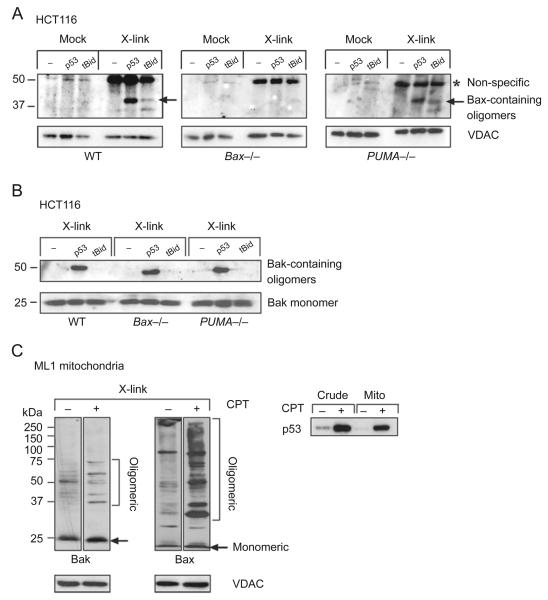
Mitochondrial p53 mediates oligomerization of Bax and Bak independently of Puma. (A, B) p53 is a potent inducer of Bax and Bak oligomerization. Subsequent to cyto C release with buffer (−), p53 (40 nM) or tBid (100 nM), HCT116 mitochondria (35 μg) were subjected to crosslinking with BMH (10 mM in DMSO for 10 min) or mock-treated (DMSO only). 1/10 of the reaction was immunoblotted for Bax (A) or Bak (B). (A) A specific band containing Bax is detected in WT and PUMA−/− but not in Bax−/− mitochondria. *Non-specific band, also present in Bax−/− cells. (B) A specific band containing Bak is detected in all genotypes. The molecular weight of ~40 kDa (Bax complex) and ~50 kDa (Bak complex) includes the possibility of homo-oligomers or hetero-oligomers with a protein X. (C) Death stimulus-induced endogenous mitochondrial p53 translocation correlates with oligomerization of mitochondrial Bak and Bax. wtp53-harboring ML1 cells were mock-treated or treated with CPT (5 μM for 3 h) to induce mitochondrial p53 translocation (right). Purified mitochondria were crosslinked and immunoblotted with N-terminal Bax and Bak antibodies (left). VDAC, mitochondrial loading control.