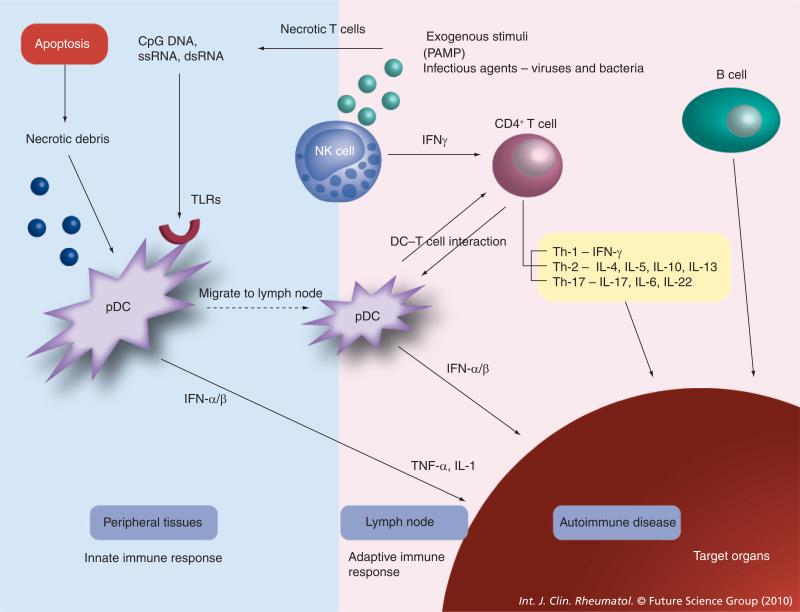
Figure 2. Role of interferons in virus-induced autoimmune disease.
Cells recognize PAMPs using pathogen recognition receptors such as TLRs. Necrotic debris from the apoptotic pathways, bacterial lipopolysaccharide, viral RNA and viral DNA act on TLRs. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells produces type 1 IFNs, which are important in host defense against viruses, and there is overproduction of IFNs in systemic lupus erythematosus. TLRs activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells leading to the release of IFN-α/β. IFN-α results in the maturation of antigen presenting cells and augmented T-cell activation, including excessive helper activity. Natural killer cells produce significant amounts of cytokines, for example IFN-γ, that can influence the development of T cells [7].
IFN: Interferon; PAMP: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; TLR: Toll-like receptor.