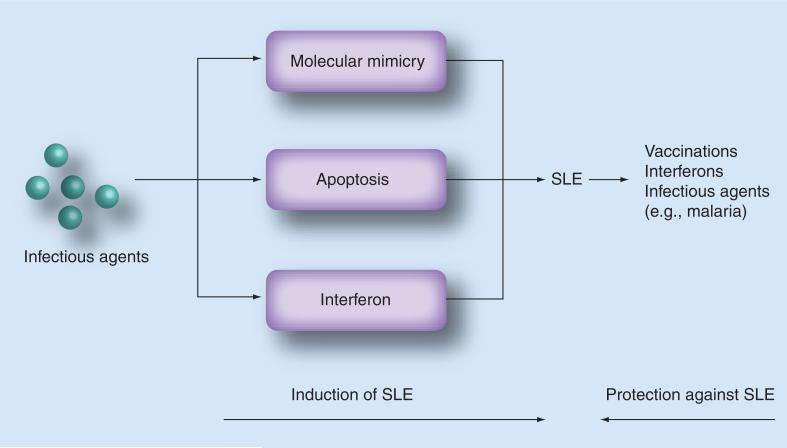
Figure 3. Mechanisms by which infectious agents induce or protect against systemic lupus erythematosus.
Infectious agents lead to the pathogenesis of SLE through several mechanisms, including molecular mimicry, apoptosis (programmed cell death) and IFN-α. On the other hand, some infections, such as malaria, can act as protective agents. Vaccinations may act as protective agents by preventing some of the infections that can induce SLE. IFN-β and IFN-γ may also have a protective effect.
SLE: Systemic lupus erythematosus.