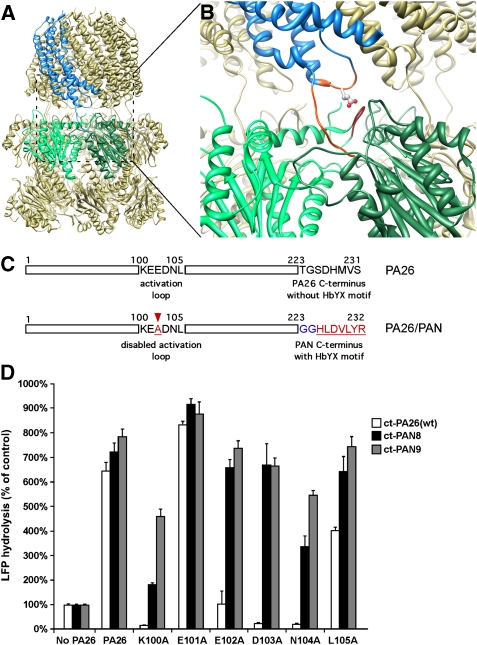
Figure 1.
Hybrid proteasomal activator PA26/PAN. (A) Atomic structure of wild-type 20S–PA26 complex (PDB ID: 1YA7, Forster et al, 2005). Two neighbouring α-subunits are coloured in light and dark green. The PA26 subunit that binds to this intersubunit pocket is coloured in blue. (B) An enlarged view of (A) shows interactions of the PA26 activation loop (orange) with the 20S reverse turn loop and the PA26 C-terminus (orange) with the 20S intersubunit pocket. The residue indicated by stick is E102. (C) Schematics shows the sequence of PA26 activation loop and its C-terminus (upper) and the design of a hybrid PA26/PAN activator (lower). (D) 20S (0.7 μg of wild-type (wt) T. acidophilum 20S) and LFP are incubated with the wt PA26 (ct-Pa26) and PA26/PAN hybrid complex with one (ct-PAN8) or two (ct-PAN9) glycine residues in the linker. The stimulation of gate opening was measured by the increase of LFP hydrolysis over the control without any activator. The values are mean±standard deviation from at least three independent measurements.