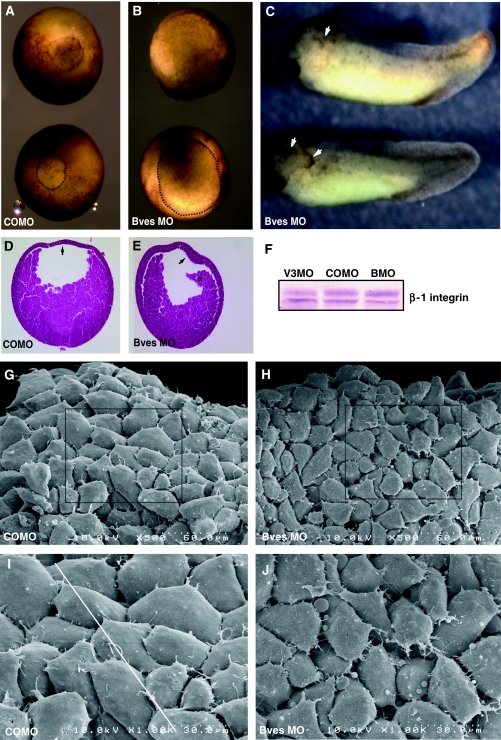
Figure 7.
Bves depletion in X. laevis embryos. Blastopore closure in embryos injected with Bves MO was decreased (B) in comparison to embryos injected with COMO (A). The blastopore is outlined in the bottom embryo in panels A and B for better visualization. Anterior defects are observed in Bves-depleted, stage-35 embryos (C), characterized by disrupted eye morphogenesis and ectodermal outgrowths (arrows). Histological staining demonstrates the BCR remains thickened (E, arrow), whereas the BCR of control embryos has thinned (D, arrow). Also, the involuting HM has become detached from the BCR in Bves-depleted embryos (E, asterisk). Integrin levels in Bves MO- or VAMP3 MO-treated embryos are similar to those in COMO-treated embryos (F). In SEM analysis of HM, COMO-injected embryos display a distinct pattern of overlapped and polarized cells (G, I, white line indicates direction of polarity), whereas Bves MO-injected embryos lack directionality, have increased spaces between cells, and exhibit irregular cell shapes (H, J; quantified in Table IV). Panels I and J show magnified views of the boxed areas in panels G and H, respectively.