Fig. 5.
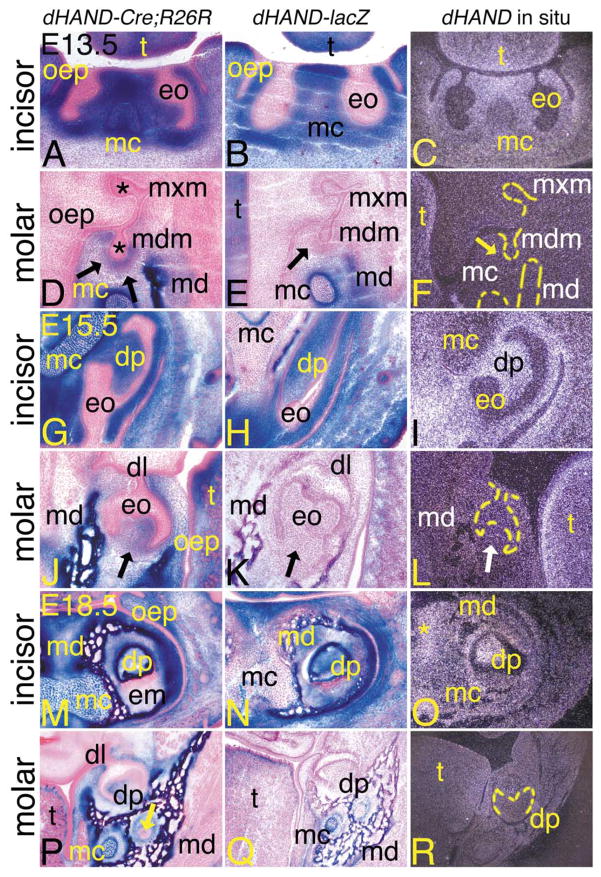
Contribution of dHAND progeny cells during odontogenesis in dHAND-Cre;R26R embryos. Transverse (A–L) and frontal (M–R) sections through the heads of dHAND-Cre;R26R (A, D, G, J, M, P), dHAND-lacZ (B, E, H, K, N, Q), and wild type (C, F, I, L, O, R) embryos. Treatment of sections was performed as described in Fig. 3. (A–C) Transverse sections through the incisors of E13.5 embryos. (A, B) Labeled cells in dHAND-Cre;R26R and dHAND-lacZ embryos are apparent throughout the developing lower jaw, including in Meckel’s cartilage (mc) and mesenchyme destined to become dentin and pulp of the lower incisors. Labeled cells are not observed in the oral epithelium (oep) or developing enamel organ (eo). (C) dHAND expression in wild type embryos is observed in the tongue (t) and mesenchyme surrounding the incisor enamel organs. Less expression is observed in Meckel’s cartilage. (D–F) Transverse sections through the molar of E13.5 embryos, showing developing dentition of the molar at the late bud stage. (D) Labeled cells in dHAND-Cre;R26R embryos are observed in the mesenchyme surrounding the bud of the developing mandibular molar (mdm; arrows) and mandibular bone (md). Oral epithelium and developing enamel organs (*) of both maxillary (mxm) and mandibular molars are unlabeled. (E) Labeled cells in dHAND-lacZ embryos are not observed surrounding the mandibular molar buds (arrow). (F) Endogenous dHAND expression is also not observed surrounding the mandibular molar buds (arrow). (G–I) Transverse sections through the incisors of E15.5 embryos. The incisors have progressed to a cap stage, approaching the “bell” configuration. (G) The nonlabeled enamel organ in dHAND-Cre;R26R embryos partially encases the labeled dental papilla (dp) and appears irregular in shape due to the transverse angle of the section. The symphysis of Meckel’s cartilage is almost completely composed of labeled cells. (H) Labeled cells in dHAND-lacZ embryos also compose most of the dental pulp of the incisor, in contrast to the mixing of labeled and unlabeled cells in the symphysis of Meckel’s cartilage. (I) dHAND expression is observed in the dental pulp and surrounding mesenchyme. Expression is much weaker in Meckel’s cartilage symphysis. (J–L) Transverse sections through the molar of E15.5 embryos. (J) In the mandibular molar, also in the cap stage, labeled cells in dHAND-Cre; R26R embryos contribute to the dental papilla (arrow), though this area also contains unlabeled cells. (K) The dental papilla of mandibular molars from dHAND-lacZ embryos is composed solely of unlabeled cells (arrow). (L) dHAND expression is not observed in the papilla of the mandibular molars (white arrow), in contrast to the strong expression in the lamina propria of the tongue. (M–O) Frontal sections through the incisors of E18.5 embryos. (M) Labeled cells in dHAND-Cre;R26R embryos appear in the dental papilla of the mandibular incisors, mandibular bone (md), Meckel’s cartilage, and surrounding mesenchyme. Oral epithelium remains unlabeled, as does the developed enamel matrix (em). (N) A similar pattern of staining is observed in the incisors of dHAND-lacZ embryos, though few labeled cells are observed in Meckel’s cartilage. (O) dHAND expression is observed in the incisor dental pulp, surrounding bone, and mesenchyme. Very little expression is observed in Meckel’s cartilage. (P–R) Frontal sections through the molars of E18.5 embryos. (P) Labeled cells in dHAND-Cre;R26R embryos appear in the dental papilla, although extensive mixing with unlabeled cells has occurred. Labeled cells are also observed in the mandibular bone, Meckel’s cartilage, and surrounding connective tissue. The residual dental lamina (dl) can be seen connecting the unlabeled oral epithelium and enamel organ. Labeled cells are not observed in mandibular nerves (arrow). (Q) Labeled cells in dHAND-lacZ embryos are confined to the mandibular bone and Meckel’s cartilage. Labeled cells are not observed in the dental papilla of the molar. (R) A low level of dHAND expression is observed in the mandibular bone surrounding the molar of wild type embryos, but expression is not observed in the molar dental pulp.