Figure 1.
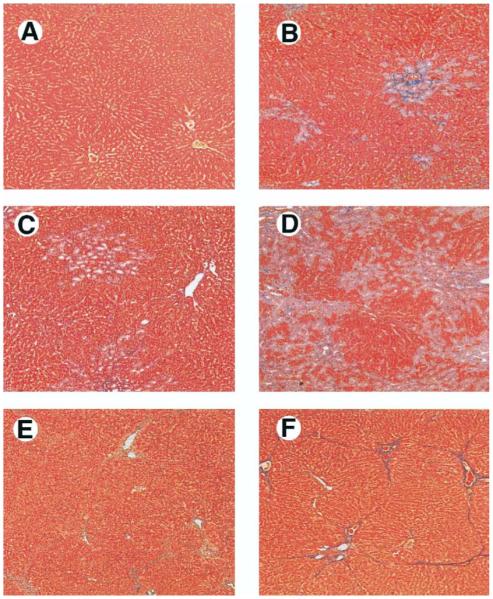
Liver histology in common bile duct ligation (CBDL)-treated and thioacetamide (TAA)-treated animals. Compared with control animals (A), 1-week CBDL animals developed bile duct proliferation and periductal fibrosis (B). Two-week CBDL animals had progressive duct proliferation with expansion of portal tracts and bridging fibrosis (C). Three-week CBDL animals developed biliary cirrhosis (D). TAA-treated animals had progression from focal hepatocyte necrosis and bridging fibrosis with minimal inflammation at 2 weeks (E) to micronodular cirrhosis at 8 weeks (F) (Masson’s trichrome stain; original magnification, 40×).
