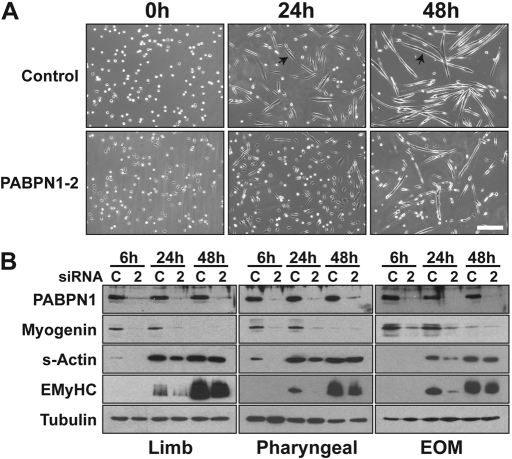
Figure 3.
PABPN1 is required for proper myoblast differentiation. Pure cultures of primary mouse myoblasts from limb, pharyngeal and extraocular (EOM) muscles were transfected with PABPN1-2 (2) or control scrambled (C) siRNA. (A) Representative phase-contrast images of limb muscle cells after 0, 24 and 48 h of differentiation (bar, 100 µm). PABPN1 siRNA cells exhibit defects in myotube formation at 24 and 48 h. Arrows indicate myotubes in control siRNA cells. (B) Protein extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting after 6, 24 and 48 h of differentiation for the differentiation markers myogenin, sarcomeric actin and embryonic myosin heavy chain (eMyHC). Knockdown of PABPN1 was also determined and alpha-tubulin was used as a loading control. Biochemical differentiation is defective in all three types of muscle cells following PABPN1 knockdown. Similar effects were observed in three independent assays.