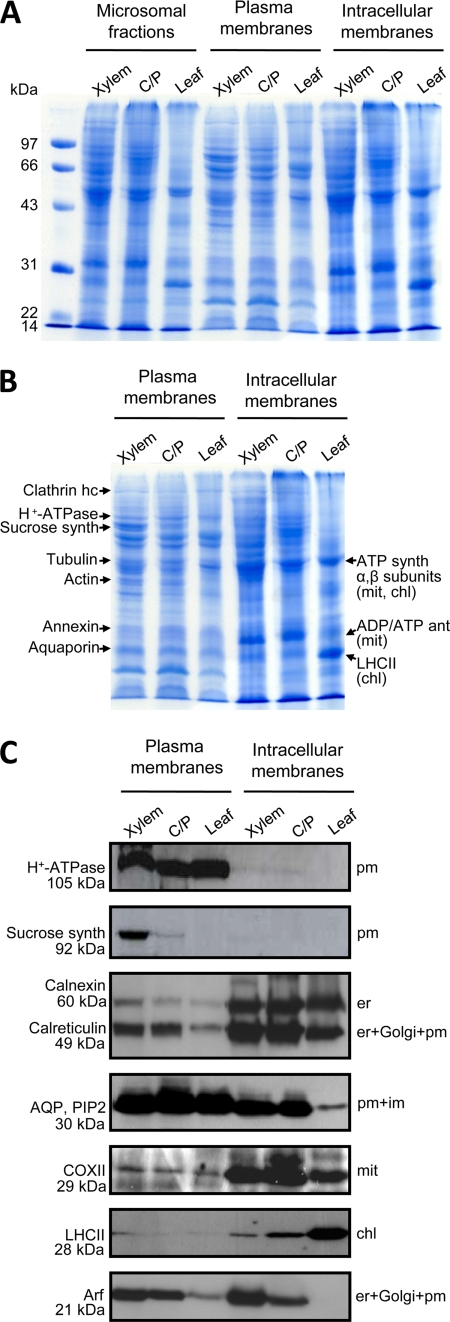
Fig. 1.
Polypeptide patterns of poplar membrane fractions and distribution of marker proteins. A, poplar microsomal fractions obtained from xylem, cambium/phloem (C/P), and leaves, respectively, were subjected to aqueous two-phase partitioning to produce plasma membrane and intracellular membrane fractions. Polypeptides were separated by SDS-PAGE (20 μg of protein/lane) and stained with Coomassie Blue. B, positions in the gel of some of the major proteins identified by mass spectrometry. C, immunoblot using sera directed against the plasma membrane P-type H+-ATPase, sucrose synthase, calnexin and calreticulin, PIP2 subfamily aquaporin, cytochrome oxidase subunit II, Photosystem II light-harvesting complex, and ADP-ribosylation factor. Expected locations for these proteins are indicated to the right. Sucrose synthase is a marker for cellulose/callose synthesis in the plasma membrane, and ADP-ribosylation factor is a marker for vesicle transport, i.e. membrane trafficking. The molecular masses given are the calculated masses and do not necessarily reflect the positions in the gel in A and B. For instance, the P-type H+-ATPase bands is next to the 97-kDa marker (compare A and B), although its isoforms have molecular masses of about 105 kDa. ant, antiporter; AQP, PIP2, PIP2 subfamily aquaporin; chl, chloroplast; COXII, cytochrome oxidase subunit II; er, endoplasmic reticulum; hc, heavy chain; im, intracellular membranes; mit, mitochondria; pm, plasma membrane; synth, synthase.