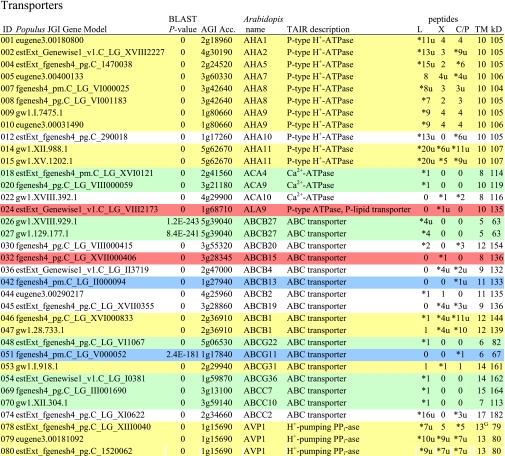
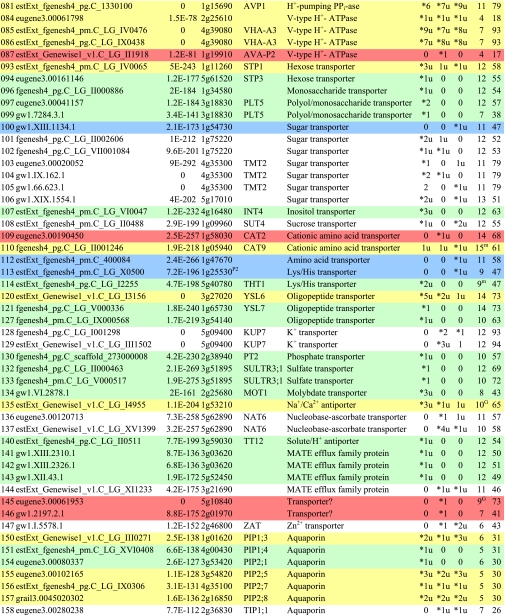
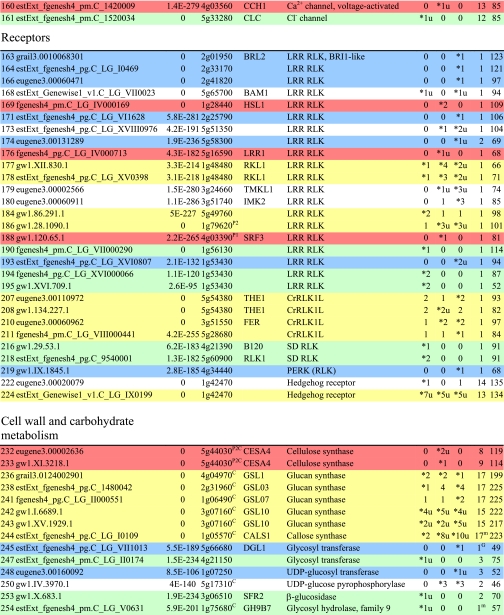
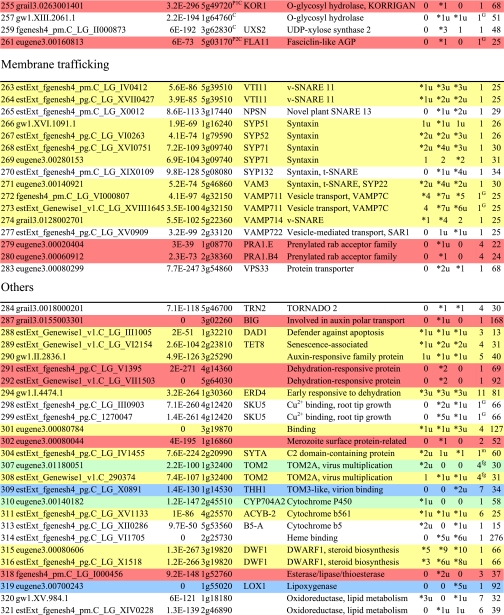
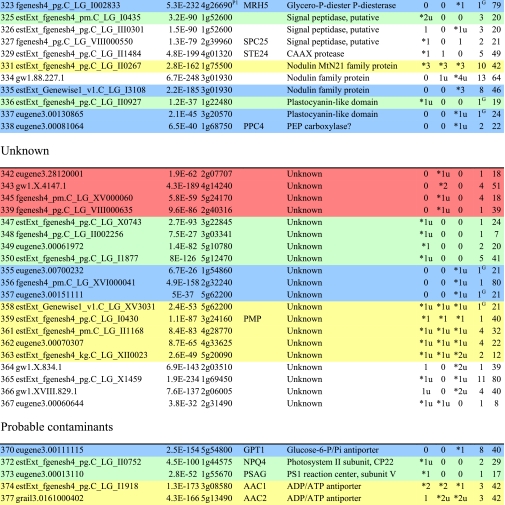
Table I. Integral membrane proteins detected by mass spectrometry in plasma membranes from leaves, xylem, and cambium/phloem.
Integral membrane proteins were identified by Phobius (38), and the number of predicted transmembrane domains (TM) are given in column 10. Proteins are grouped according to function and identified by an ID in column 1, also used in figures and text. Only top rank proteins are included, and the number of peptides identifying each protein is given in columns 7–9 for plasma membranes from leaves (L), xylem (X), and cambium/phloem (C/P), respectively; a number followed by “u” indicates that at least one peptide unique to the protein was found, and a star indicates that the protein is classified as top rank in that tissue. The color code is yellow for proteins found in the plasma membranes from all three tissues and green, red, and blue for proteins found only in leaf, xylem, and cambium/phloem plasma membranes, respectively. All annotation is via the Arabidopsis database at TAIR. Thus, amino acid sequences corresponding to identified gene models in the poplar database (column 2) were blasted against the Arabidopsis database to identify the closest Arabidopsis homolog of each protein, which is identified by its AGI accession number (column 4) followed by its short name in column 5 and description in column 6. Blast p values (column 3) are included to indicate how well the poplar and Arabidopsis amino acid sequences agree. The calculated molecular mass in column 11 is from Mascot. Arabidopsis genes previously suggested to be involved in cell wall formation are indicated in column 4. Predicted lipid anchors are indicated in column 10. For ABC transporters, the new nomenclature according to Verrier et al. (2) was used, and for RLK receptors, we used the nomenclature in Shiu and Bleecker (5). For a complete list of integral proteins including the subset, see supplemental Table 2. PM, plasma membrane; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; MATE, multidrug and toxin extrusion.
C Gene present in the Cell Wall Navigator database (11).
P1 Highly coregulated gene for At CESA1, -3, and -6, i.e. primary cell wall formation (12).
P2 Highly coregulated gene for At CESA4, -7, and -8, i.e. secondary cell wall formation (12).
G GPI.
m Myristoyl.
g Geranylgeranyl.
f Farnesyl (predictions described in Ref. 49).