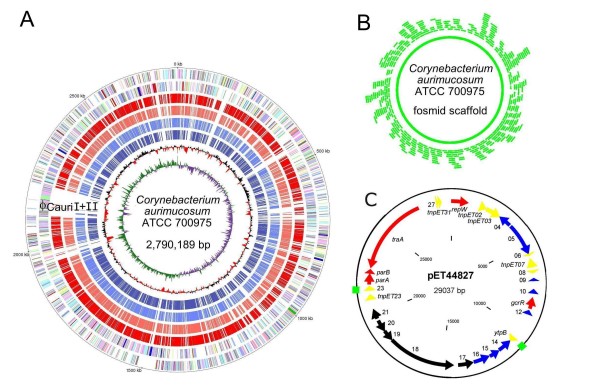
Figure 1.
The complete genome of the clinical isolate C. aurimucosum ATCC 700975. (A), Plot of the C. aurimucosum ATCC 700975 chromosome. The circles represent from the outside: circle 1, DNA base position; circles 2 and 3, predicted protein-coding sequences transcribed clockwise and anticlockwise, respectively; circles 4 to 7, genes encoding orthologous proteins in C. diphtheriae NCTC 13129, C. jeikeium K411, C. urealyticum DSM7109, and C. kroppenstedtii DSM44385; circle 8, G+C content plotted using a 10-kb window; circle 9, G/C skew plotted using a 10-kb window. The predicted protein-coding sequences are coloured according to their functional classification into the Clusters of Orthologous Groups of proteins [93]. The genomic position of the putative prophages ϕCauri I and ϕCauri II is marked. (B), Fosmid scaffold of the C. aurimucosum ATCC 700975 chromosome. Individual fosmid clones used to build the genomic scaffold by terminal insert sequencing are represented as green segments. (C), Genetic map of plasmid pET44827 detected in C. aurimucosum ATCC 700975. The predicted protein-coding regions are shown by arrows indicating the direction of transcription. A direct repeat region is indicated as green box. Colour code: black, non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) gene region; yellow, transposase genes and repetitive sequences; red, genes involved in plasmid replication and maintenance; blue, genes encoding hypothetical proteins.