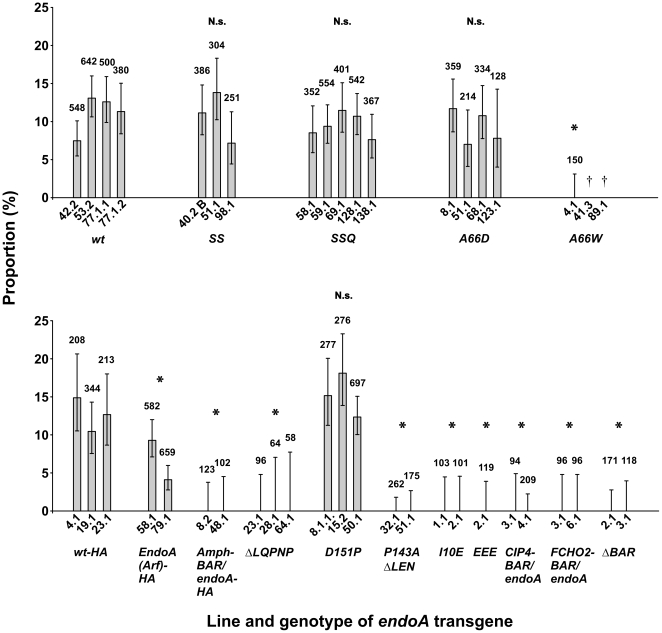
Figure 2. Ability of transgenic endoA constructs to rescue the development of endoA null mutants to adulthood.
Shown is the proportion of eclosed adult rescuants (genotype elav-GAL4/Y or w; UAS-endoA*/+; endoAΔ4/endoAΔ4) relative to the total number of adult progeny resulting from the rescue cross. The UAS-endoA* transgene carried the mutations indicated on the abscissa and in some cases also encoded a hemagglutinin epitope tag (indicated by the suffix “−HA”). Also shown is the proportion of rescuants in which the endoA transgene encoded either wild type EndoA (“wt”), or HA-tagged wild type EndoA (“wt-HA”). Each bar represents one transgenic integration line, specified below the abscissa. The total number of adult progeny resulting from the rescue cross is indicated for each line (numbers above the bars). The lower and upper 95% confidence intervals are given. * P<0.01. N.s., not significant. †Besides UAS-endoAA66W 4.1, the rescue efficiency of two other UAS-endoAA66W transgenes was evaluated (UAS-endoAA66W 41.3 and UAS-endoA89.1). They both caused lethality of all the progeny from the rescue cross, as detailed in the text.