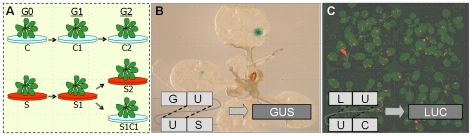
Figure 1. Experimental set-up.
A. Arabidopsis plants (G0) were propagated to the next generation (G1) under normal growth conditions (C1) or in the presence of stress (S1 for ‘stressed, generation 1’). Next, the S1 plants were propagated to G2 in the presence of stress (S2) or under normal conditions (S1C1). The C1 plants were propagated to G2 under normal conditions (C2). B–C. Plants used in the experiment carried in the genome β-glucuronidase (GUS) or luciferase transgenic marker genes serving as a homologous recombination substrate. Double strand break in the region of homology (depicted as ‘U’) can potentially be repaired via homologous recombination using the second region of homology as a template. This restores the active transgene. Cells and their progeny in which recombination events occurred can be visualized via either histochemical staining (GUS) (B) or via CCD camera (LUC) (C). Individual events are then scored in the population of 20–200 plants and expressed as an average number per single plant.