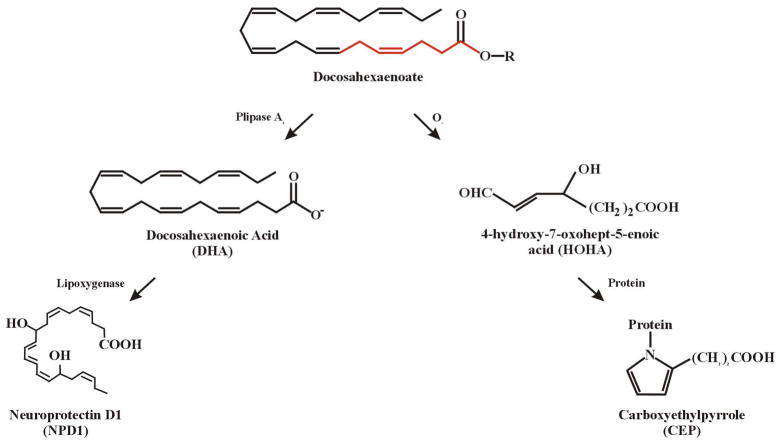
Figure 4.
Enzymatic and oxidative mechanisms of docosahexaenoate metabolism and degradation. The esterified form of DHA (docosahexaenoate) is converted to free DHA by phospholipase activity. A lipoxygenase then forms picomolar levels of neuroprotectin D-1 (NPD1), primarily in RPE cells. Molecular oxygen reacts with docosahexaenoate to form a 7 carbon reactive aldehyde intermediate (HOHA) that is capable of forming carboxyethylpyrrole (CEP) protein adducts. The first 7 carbons in docosahexaenoate (shown in red) give rise to HOHA; R= glycerophospholpid esterified with DHA.