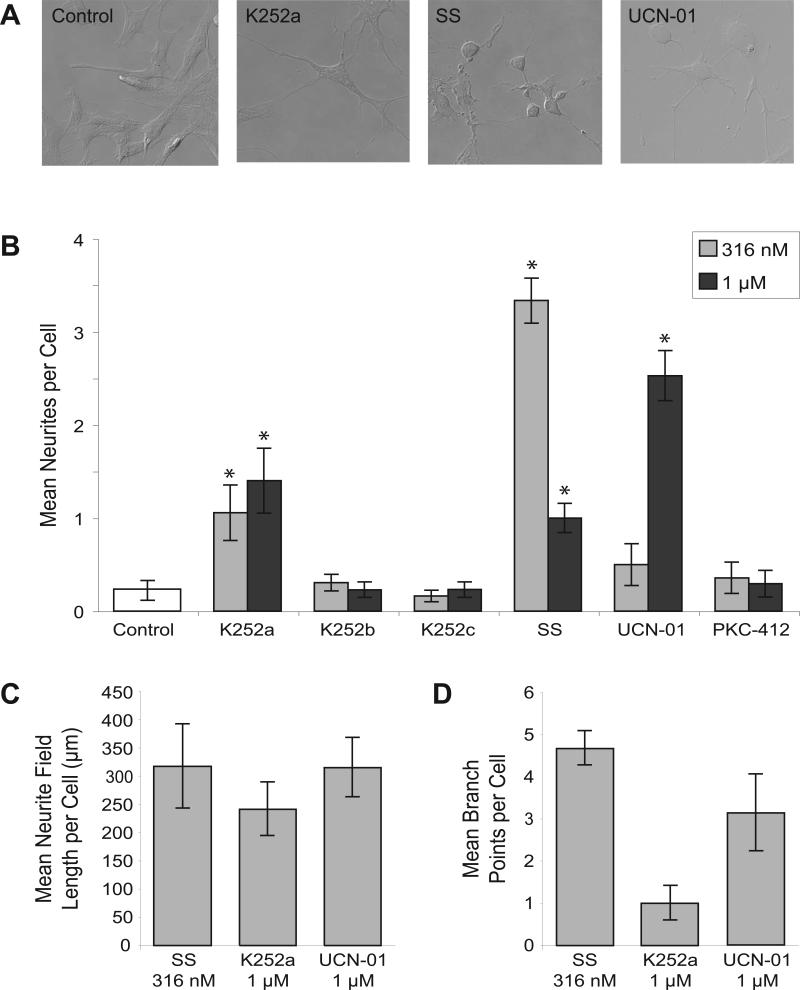
Figure 1. Staurosporine (SS), K252a, and UCN-01 induce morphological differentiation in RGC-5 cells.
(A) Cells treated with SS or UCN-01 exhibit a morphology similar to primary RGCs, including neurites and rounded somas. Treatment with K252a induces extension of broader, flatter neurites than those seen in SS-differentiated cells, and no somal rounding. (B) SS differentiates RGC-5 cells most effectively at a concentration of 316 nM (resulting in 3.3 ± 0.2 primary neurites per cell), while UCN-01 is most effective at a 1 μM concentration (2.5 ± 0.3 primary neurites per cell). (C) Cells treated with K252a extended neurites with a mean field length slightly but statistically insignificantly shorter than mean field lengths per cell of staurosporine or UCN-01 treatment. (D) Neurites induced by K252a were noticeably but insignificantly less complex than those induced by staurosporine or UCN-01 (1.0 ± 0.4 branch points per cell after K252a treatment vs. 4.7 ± 1.3 and 3.1 ± 0.9 branch points per cell after staurosporine or UCN-01 treatment respectively, p = 0.11).