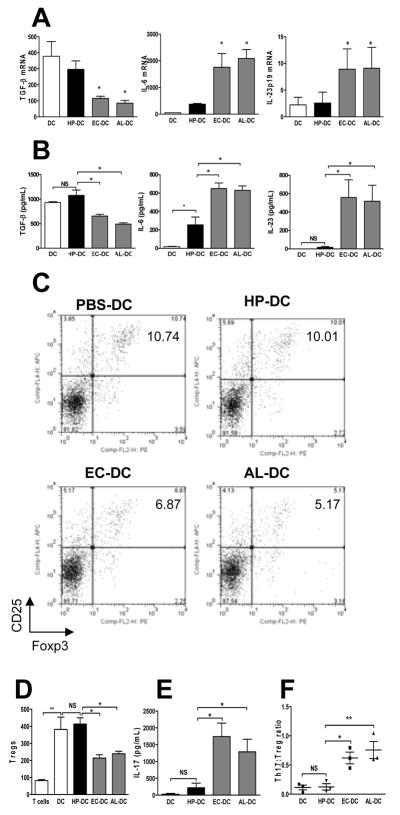
Figure 3. Bone marrow–derived dendritic cells (DCs) maintain a low Th17:Treg ratio with H pylori stimulation.
Bone marrow–derived DCs were pulsed with live H pylori, E coli, or A lwoffii for 18 h (denoted HP-DC, EC-DC, and AL-DC, MOI 1:100) and DC cytokine PCR-array was used to determine mRNA expressions of DC immunomodulatory genes (see Materials and Methods). Supernatants were collected and protein expression was measured by ELISA. (A) Comparison of TGF-β, IL-6, and IL-23p19 mRNA expressions of DCs using quantitative PCR. (B) Release of TGF-β, IL-6, and IL-23 by DCs was measured by ELISA. Messenger RNA and protein cytokine expressions indicate that lower levels of IL-6 and IL-23 were expressed by HP-DC compared with EC-DC and AL-DC. TGF-β production by DCs was similar in PBS-DC and HP-DC but reduced in EC-DC and AL-DC. A 72-h mixed leukocyte reaction using DCs and naive syngeneic splenocytes further assessed DC function in Treg and Th17 induction. (C) The percentage of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs in the total number of CD4+ T cells was determined using FACS-generated dot plots. (D) The relative numbers of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs from three separate experiments. (E) IL-17 production measured by ELISA. (F) The Th17:Treg ratio was calculated by dividing the number of IL-17 produced CD4+ cells by the number of Foxp3+ CD4+ cells measured using intracellular FACS staining. The Th17:Treg ratio was lower in HP-DC than in EC-DC and AL-DC (n = 3).