Figure 1.
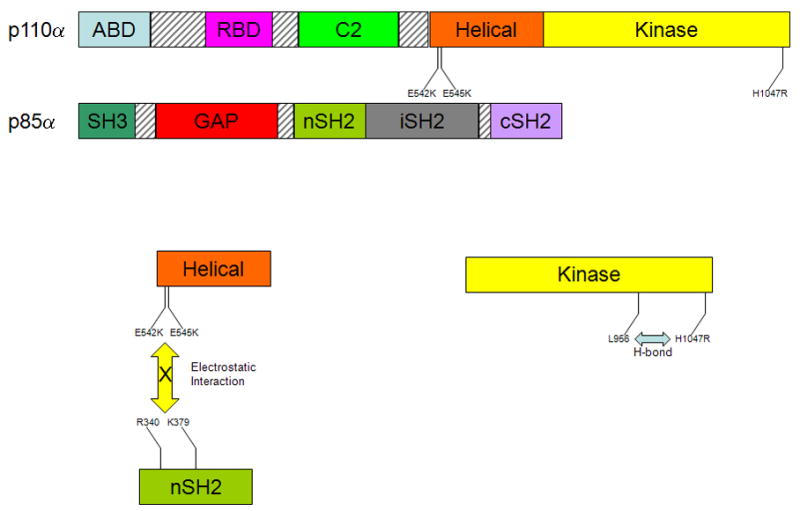
A representation of the domains of the PI3K subunits p110α and p85α. The p110α catalytic subunit has 5 domains including adaptor-binding domain (ABD), the Ras-binding domain (RBD), a calcium binding domain (C2), a helical domain and a kinase domain. The p85α regulatory subunit contains 5 domains as well, which include a Src homology 3 domain (SH3), a GTPase activating protein domain (GAP), an N-terminal Src homology 2 domain (nSH2), an inter- Src homology 2 domain (iSH2), and a C-terminal Src homology 2 domain (cSH2). The exon 9 hotspot mutations, E542K and E545K, occur in the helical domain of the catalytic subunit p110α, and the charge reversal caused by these mutations inhibits electrostatic interactions between those amino acids on the p110α helical domain and R340 and K379 on the nSH2 domain of p85α. The exon 20 hotspot mutation, H1047R, is in the kinase domain of p110α, and this mutation has been proposed to form a hydrogen bond with L956 of p110α, which in turn leads to catalytic activity of p110α.
