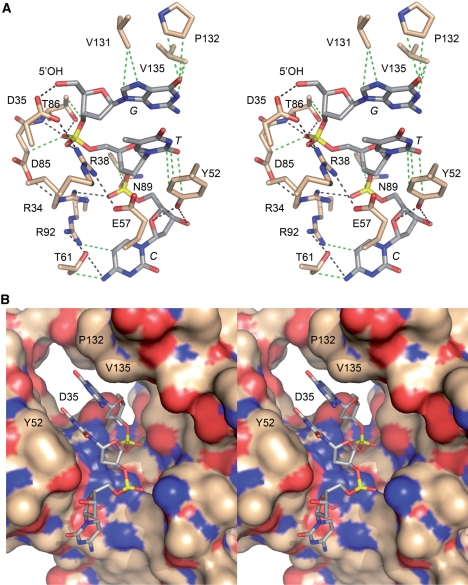
Figure 1.
The 5′-OH polynucleotide acceptor site of T4 Pnkp. (A) A stereo view of the kinase active site is shown, highlighting enzymic contacts to a trinucleotide 5′-OH phosphate acceptor (PBD ID code 1RC8). The side chains that were subjected to mutational analysis here and previously are shown in stick representation with carbons colored beige; the residue numbers are specified. The 5′-GTC trinucleotide is depicted as a stick model with carbons colored gray and the nucleobases labeled in italics. Hydrogen-bonding and ionic interactions are depicted as black dashed lines. van der Waals contacts are depicted as green dashed lines. (B) Stereo view of the phosphate acceptor tunnel of the kinase domain with the protein rendered as a surface model and the 5′-GTC trinucleotide depicted as a stick model. The deep end of the tunnel is demarcated by Asp35, which coordinates the 5′-OH. Also labeled are Tyr52, which contacts the second and third nucleosides, and Val131 and Pro132, which contact the first nucleobase. The figure highlights the narrow tunnel aperture, which allows ingress of single-stranded nucleic acid, but would seem to exclude a nucleic acid duplex.