Figure 4. dimm Misexpression Transforms the Vesicle Phenotype of R1-R6 Photoreceptor Terminals.
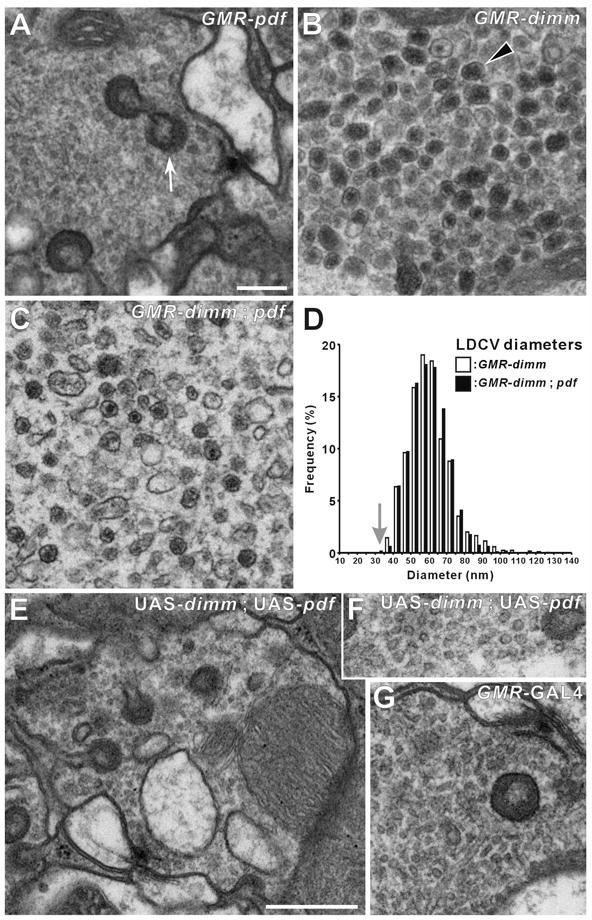
(A–C and E–G) EMs of R1-R6 terminals. (A) GMR > Pdf. (B) GMR > dimm. (C) GMR > dimm, Pdf. Ectopic large dense-core vesicles (LDCVs: arrowhead in B) appear in the terminals of single GMR > dimm (B) and double GMR > dimm, Pdf (C) UAS transgenic lines, but are lacking in the control GMR > Pdf (A). Capitate projection profiles (arrow, in A) identify profiles of R1-R6 terminals. (D) Distribution of the diameters of these ectopic LDCVs in genetically-transformed photoreceptor cells, either without (as in B) or with (as in C) Pdf. LDCV profile diameters in GMR > dimm and in GMR > dimm, Pdf flies have similar distributions that peak at about 60 nm, far larger than the mean of the small clear synaptic vesicles in an isoparental control, UAS-dimm fly (arrow). (E–G) Isoparental controls (UAS-dimm, UAS-Pdf) (E and F) and GMR-GAL4 (G), have small, clear synaptic vesicles, presynaptic T-bar ribbons, and capitate projections. Such normal synaptic phenotypes were also seen in terminals of photoreceptors misexpressing Pdf alone (A). Scale bars: 200 nm in A (also applies to B, C, F, and G); 500 nm in E.
