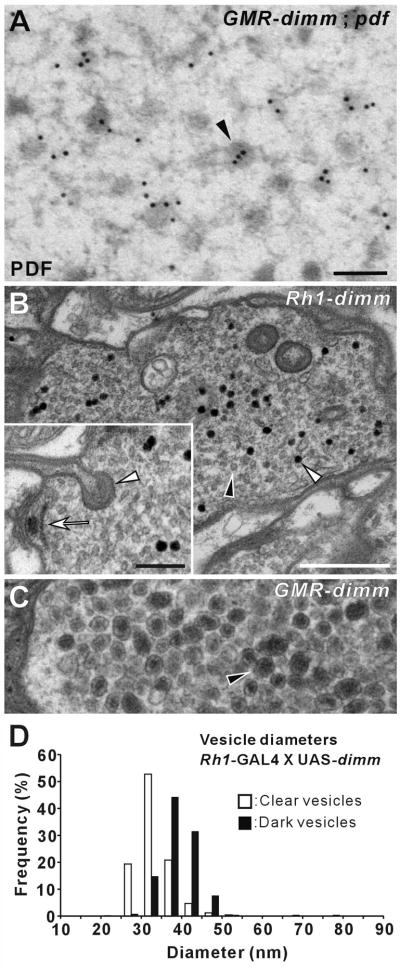
Figure 5. GMR- and Rh1-GAL4 Driver-Dependent DIMM-Transformed Vesicle Phenotypes.
(A–C) EMs of the lamina terminals of R1-R6. (A) Immunogold labeling with anti-PDF on a photoreceptor terminal from a GMR > dimm, Pdf fly. Large dense-core vesicles (LDCVs: arrowhead) in photoreceptor terminals transformed by dimm and Pdf co-misexpression are immunoreactive to PDF peptide. (B) Rh1 >dimm alone caused a population of slightly larger, dark vesicles (open arrowhead) to appear among normal clear synaptic vesicles (filled arrowhead). Compare the latter, shown at higher magnification in the inset, with the size of ectopic LDCVs (arrowhead) in GMR > dimm R1-R6 (C), at the same magnification. Note that Panel C is a portion of the same image shown in Figure 4B. Although a different type of vesicle formed in Rh1 > dimm R1-R6, the terminals had presynaptic T-bar ribbons (arrow: inset in B) and capitate projections (arrowhead: inset in B), just as in controls, but largely absent in GMR > dimm R1-R6. (D) Distribution of profile diameters of small, clear (open bars) and dark (closed bars) vesicles in R1-R6 genetically transformed by dimm misexpression under regulation of Rh1-GAL4 driver (as in B). The distribution was calculated from measurements of 1,432 clear and 251 dark vesicle profiles. Scale bars: 100 nm in A; 500 nm in B; 200 nm in inset of B (also applies to C).