Figure 1.
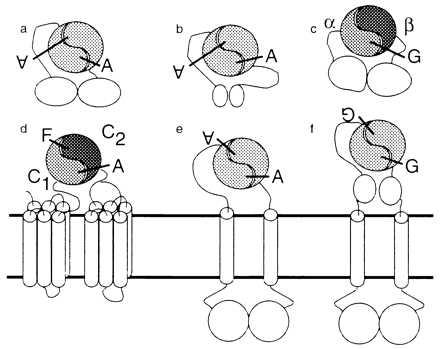
Topologies (3) of yeast AC (a), bacterial class III AC (b), sGC (c), mammalian and Drosophila ACs and ACA (d), ACG and parasite ACs (e), and ANP receptor and photoreceptor GCs (f). A, ATP; G, GTP; and F, forskolin. Mammalian ACs and their homologues are known as “class III” (3) to distinguish them from nonhomologous class I and II bacterial ACs.
