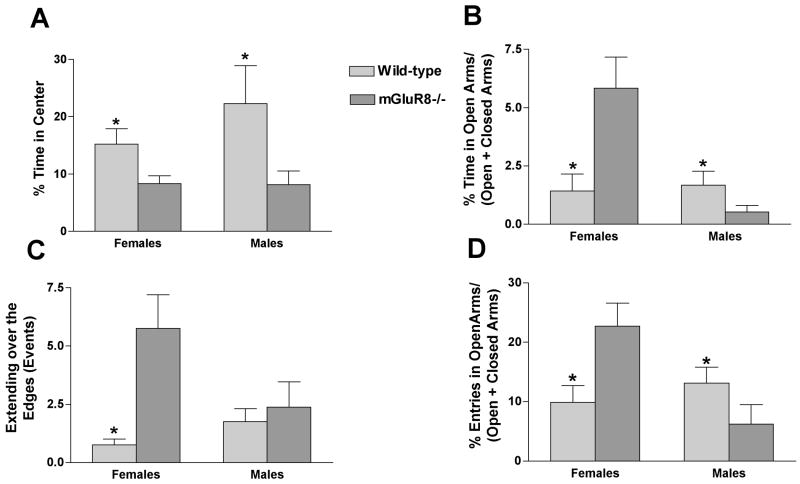
Fig. 1.
Measures of anxiety in mGluR8-/- and wild-type female and male mice in the open field (A) and elevated plus maze (B-D). A. mGluR8-/- female and male mice spent less time in the more anxiety-provoking center of the open field. B. mGluR8-/- female mice spent more time in the anxiety-provoking open arms of the elevated plus maze, while mGluR8-/- male mice spent less time in open arms of the elevated plus maze. C. mGluR8-/- female mice spent more time over the open arms of the elevated plus maze than sex-matched wild-type mice. D. mGluR8-/- female mice entered open arms of the elevated plus maze more often than sex-matched wild-type mice, while mGluR8-/- male entered the open arms of the elevated plus maze less frequently than sex-matched wild-type mice. n = 8 mice/genotype/sex. *p < 0.05 versus sex matched wild-type control.