Fig. 5.
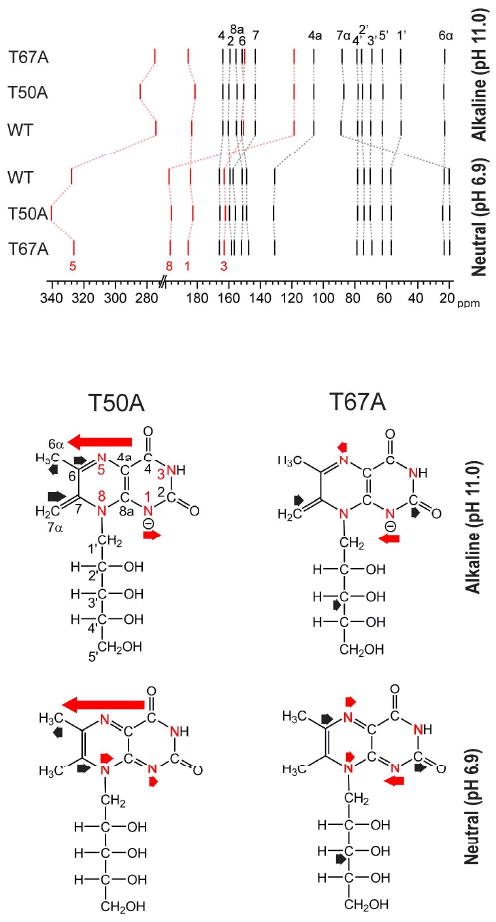
Top, 13C chemical shifts (black) and 15N chemical shifts (red) of 1 in complex with the N-terminal domain of riboflavin synthase [wild type (WT) or mutant as indicated]. In the bottom part of the figure, the impact of point mutations on the chemical shifts of neutral 1 and its exomethylene anion (8) is shown by arrows (13C shift changes, black; 15N shift effects, red).
