Figure 4.
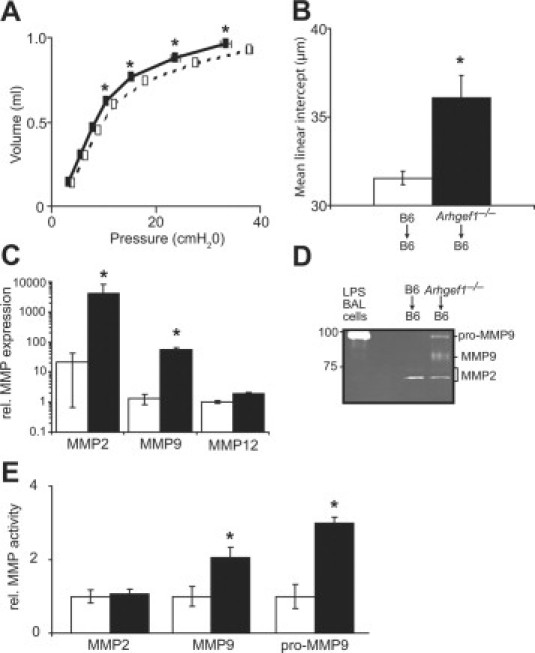
Transfer of Arhgef1-deficient BAL cells causes pathology in adult lungs. Eight-week-old wild-type mice received intratracheal instillations of BAL cells recovered from either C57BL/6 mice or Arhgef1-deficient mice once a week for 4 weeks. A: Quasi-static pressure-volume loops performed on wild-type mice that received either wild-type BAL cells (open boxes, dotted lines, n = 5) or Arhgef1−/− BAL cells (solid boxes, solid lines, n = 9). Data represent mean ± SE. B: Mean linear intercept (μm) of alveolar septae as measured on H & E–stained inflated lungs from wild-type mice that received either wild-type BAL cells (open bar, n = 5) or Arhgef1−/− BAL cells (solid bar, n = 9). C: MMP2, MMP9, and MMP12 expression measured by qPCR in BAL cells recovered 48 hours after the transfer of peritoneal macrophages from wild-type (n = 4) and Arhgef1−/− (n = 7) into wild-type recipient mice. D: Representative gelatin zymography of BAL supernatant recovered from mice described in C. Whole cell lysate of BAL cells from LPS-treated wild-type mouse is included as positive control for pro-MMP9. E: MMP activity in BAL supernatant from mice described in C as determined by densitometric analysis. MMP activity is shown as fold relative to control samples. Data represent mean ± SE. *P < 0.05 for Student two-tailed t test comparing mice that received wild-type cells to mice that received Arhgef1−/− cells.
