Figure 5.
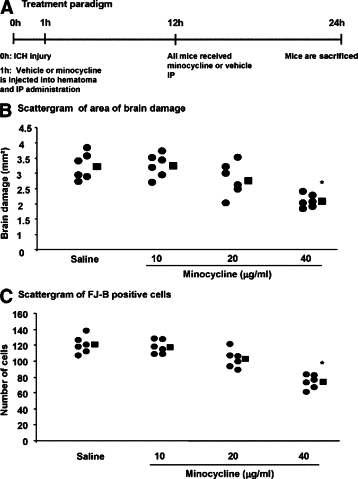
Brain damage and neuronal death after ICH are reduced by minocycline administered locally from 1 hour after injury (A). In B and C, each circle represents individual mice while the square depicts the average of the group (six mice per group). The quantitative data show that brain damage areas (B) and neuronal death (C) are reduced by minocycline at 40 μg/ml compared with intracerebral administration of PBS (*P < 0.05), but lower concentrations of minocycline (10 and 20 μg/ml) did not reach statistical significance (P > 0.05).
