Figure 5.
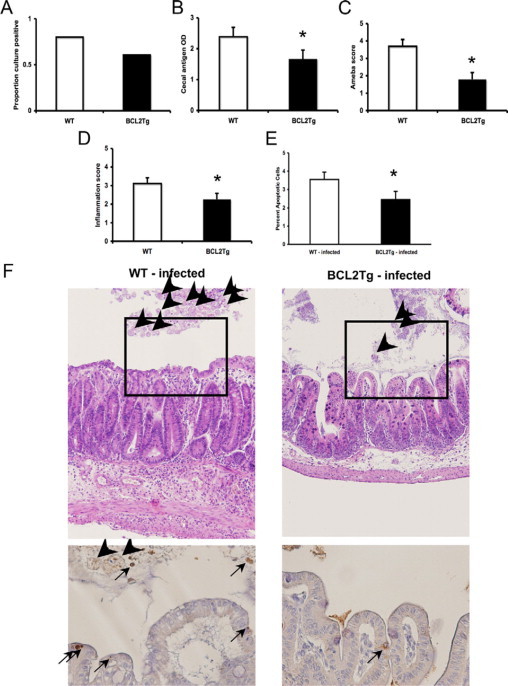
Intracecal challenge of Bcl-2 transgenic mice. Male FVB mice transgenic for epithelial expression of Bcl-2 (Bcl-2Tg) and wild type (WT) littermates were challenged intracecally with 2 × 106E. histolytica trophozoites and sacrificed after 5 to 7 days. Cecal contents were assessed for the presence of amoeba by culture (A) and E. histolytica antigen by ELISA (B). Cecal tissue was stained with H&E and scored in blinded fashion for the presence of amoeba (C) and degree of inflammation (D) as detailed in Materials and Methods. E: Rates of apoptotic cells in the cecum were measured histologically in the infected mice from each group (n = 22 and 15 for WT and Bcl-2Tg mice, respectively). Data are shown as mean ± SE from six experiments. *P < 0.05, n = 28 and 25 for WT and Bcl-2Tg mice, respectively. F: Representative photomicrographs of WT-infected versus Bcl-2Tg-infected cecal tissue at day 5 postchallenge are shown. Top row are H&E stained slides (original magnification, ×100) showing more inflammation, cecal thickness, and amebic trophozoites (arrowheads) in WT mice. Bottom are caspase 3 stained slides at ×400 (original magnification). In WT mice, apoptotic cells are apparent within the epithelial layer (arrows) frequently in juxtaposition with amebic trophozoites (arrowheads).
