Figure 3.
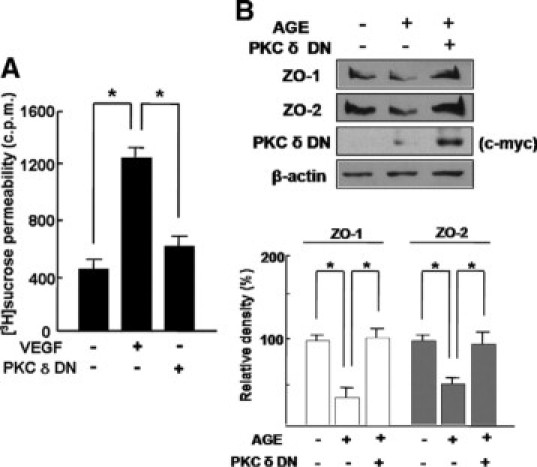
Inhibition of PKC δ by PKC-δ-DN attenuates VEGF-induced hyperpermeability and loss of tight junction proteins under diabetic condition in HRMECs. A: VEGF, 20 ng/ml, was treated for 6 hours in HRMECs with or without transfection of PKC-δ-DN plasmid. [3H]sucrose permeability assay in HRMECs was measured as counts per minute (c.p.m.). Each point represents the mean (±SD) of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. *P < 0.05. B: HRMECs were transfected by PKC-δ-DN plasmid. Cells were subsequently cultured for 48 hours to allow for detectable protein expression and were additionally incubated for 12 hours in AGE treatment. The expression of ZO-1 and ZO-2 was assessed, and transfection of PKC-δ-DN was confirmed by expression of c-myc. β-Actin was served as the loading control. Figures were selected as representative data from three independent experiments. Quantitative analysis was performed by measuring protein expression relative to the control. Each point represents the mean (±SD) of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. *P < 0.05.
