Figure 1.
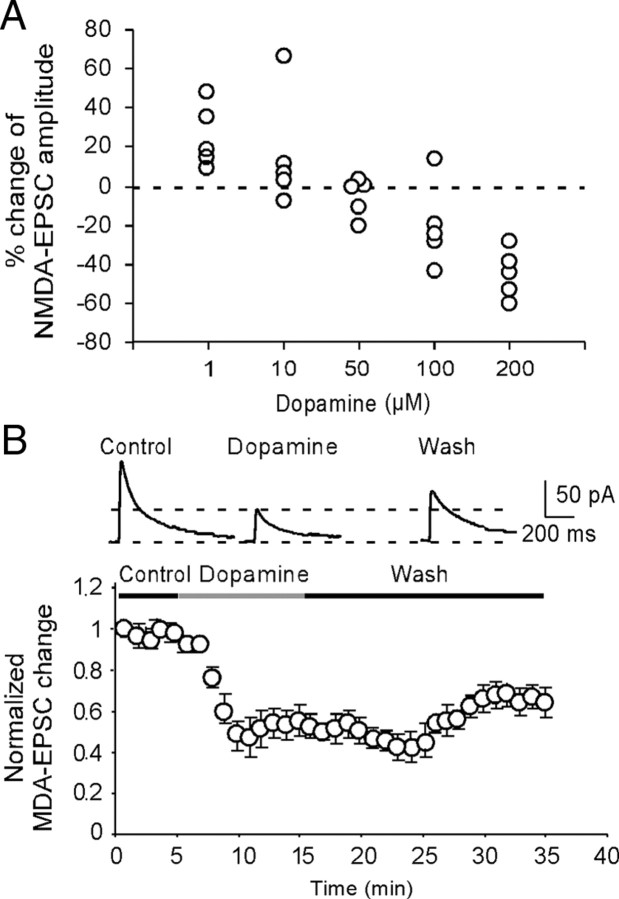
DA induces bidirectional dose-dependent effects in synaptically evoked NMDA-EPSCs in layer 5 pyramidal neurons. A, Dose–response relationship for the effects of DA. The data were average effects of DA on NMDA-EPSCs determined at 10 min after DA application (n = 5 for each dose). B, Top panel, Examples of the NMDA-EPSCs recorded in presence of NBQX (20 μm) and picrotoxin (50 μm) in control, dopamine, and washout period. The representative traces indicated that high-dose DA (200 μm) significantly reduced the amplitudes of NMDA-EPSCs. Bottom panel, Summary graph showing the time course of high-dose (200 μm) DA effects on the amplitude of NMDA-EPSCs. This suppressing effect on NMDA currents was long-lasting with little recovery even after 15–20 min washout, suggesting the possibility of NMDA receptor internalization under this condition. Note that the data were normalized to the baseline EPSCs recorded in the first minute. Error bars indicate SEM.