Figure 3.
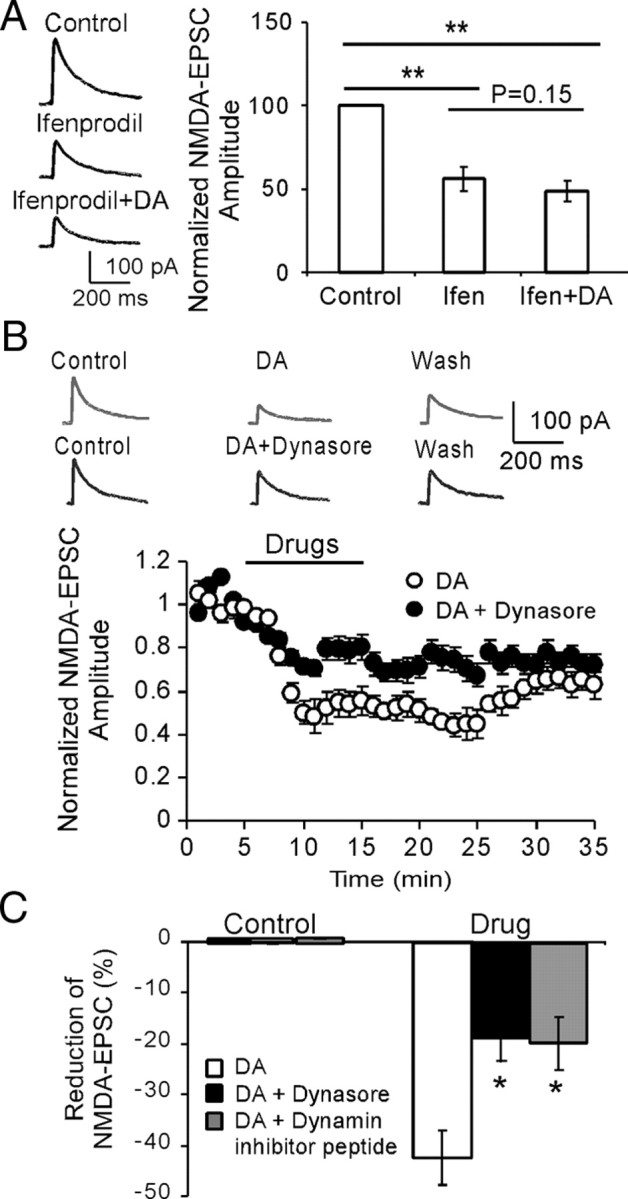
High-dose DA-induced reduction of NMDA-EPSCs is partially dependent on dynamin-mediated internalization of NR2B subunits. A, Left panel, Sample traces showing the effects of NR2B antagonist ifenprodil (3 μm) and ifenprodil plus dopamine (200 μm) on NMDA-EPSCs. Right panel, Initial application of NR2B antagonist ifenprodil significantly decreased the amplitudes of NMDA-EPSCs (p < 0.01), whereas followed coapplication of ifenprodil with DA did not cause significant attenuation on the NMDA-EPSCs (p = 0.15), suggesting the involvement of NR2B subunits. B, Sample traces (top panel) and time course data (bottom panel) showing the effects of dynasore, a potent membrane-permeable inhibitor of endocytosis, on DA-induced inhibition of NMDA receptors (n = 6). C, The inhibitory effects of DA on NMDA-EPSCs were significantly blocked by dynamin inhibitory peptide (50 μm in pipette) and dynasore (100 μm in bath), which prevent receptor endocytosis (n = 6; p < 0.05 for both). Error bars indicate SEM.
