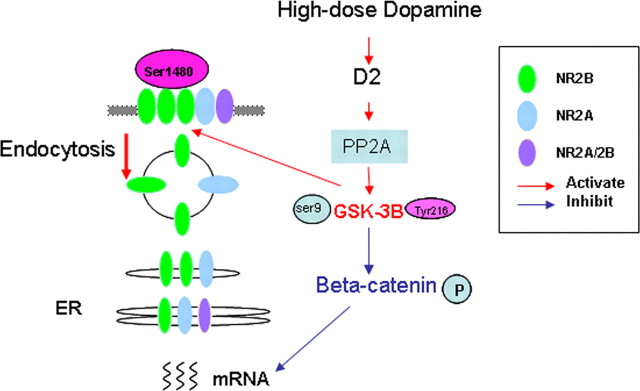
Figure 9.
Schematic graph showing the signaling pathway involved in hyperdopamine/D2-mediated inhibition of synaptic NMDA receptors. High concentration of DA/activation of D2 receptor activates GSK-3β via its upstream regulator PP2A. GSK-3β in turn phosphorylates β-catenin (Ser33/37/Tyr41), which interacts with NR2B, controls the NR2B gene transcription, and thus affects the protein synthesis of NR2B subunits. Phosphorylation of NR2B-Ser1480 and dynamin play an important role for NR2B endocytosis in the DA-induced inhibition of NMDA current.