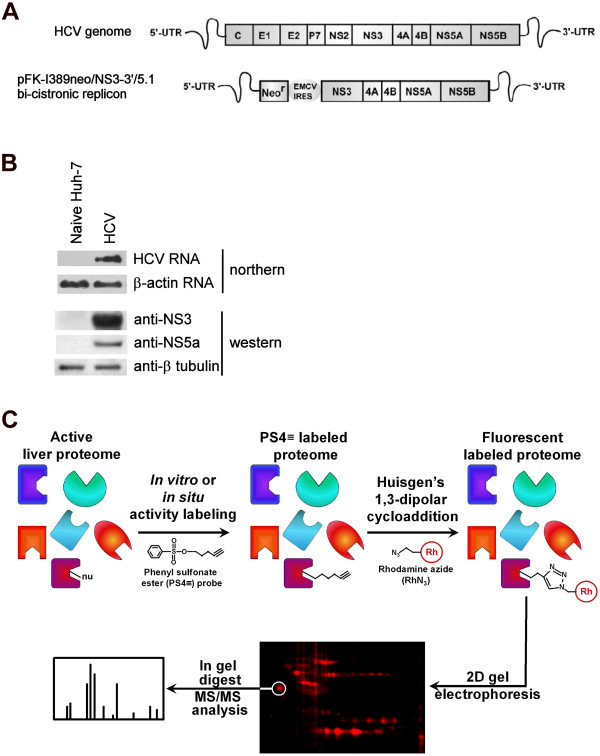
Figure 1.
Structure and protocol of the PS4≡ probe used in vitro and in situ to target the active Huh-7 proteome during HCV replication. (A) Schematic representations of the HCV genome and the bi-cistronic (pFK-I389neo/NS3-3'/5.1) subgenomic replicon used in this study (NS, non-structural proteins). (B) Northern analysis of HCV and β-actin (as a loading control) RNA (upper two blots) and detection of HCV NS3, HCV NS5A, and β-tubulin (as a loading control) proteins by western blotting (lower three blots) in naïve Huh-7 human hepatoma cell lines and in Huh-7 cells stably replicating HCV (HCV). (C) Scheme of the ABPP protocol used to identify phenyl sulfonate ester (PS4≡) targets. The active proteome of naïve Huh-7 cells (not shown) or Huh-7 stably expressing the HCV replicon was labeled through a nucleophilic (Nu) residue within the active site of the enzyme targeted by the reactive group of the PS4≡ probe. After isolation, the labeled proteome was conjugated with the rhodamine azide reporter tag (RhN3) via the Huisgen's 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition and separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. The fluorescently tagged proteins were identified by LC-MS/MS.